Tales from Los Angeles’ lost French quarter and Southern California’s forgotten French community.
Thursday, January 26, 2017
Georges Le Mesnager: LA's Favorite Fighting Frenchman
In July of 1870, the Franco-Prussian War broke out. Travel time and expenses be damned, nineteen-year-old Georges immediately packed up and went back to France to enlist in the French Army and defend his homeland under General de Chanzy.
Georges returned to LA after the war ended, and became a U.S. citizen at age 21. He worked as a notary and court translator (remember, French was more commonly spoken than English in 1870s LA), owned a store on Commercial Street, and owned property at 1660 N. Main Street.
Georges married Concepción Olarra (sometimes styled "O'Lara"). It isn't clear whether she was Mexican, Spanish, or born in the New World to Spanish parents - and it's possible she had Irish ancestry. Unfortunately I cannot find any records of her birth or death. Records on Ancestry do show other Olarras (none of whom I could conclusively tie to Concepción) living in 19th century Mexico.
Letters published in La Crónica between 1876-1878 indicate that Concepción was probably a native Spanish speaker. This would not have been a deterrent to the multilingual Georges. They had four children: Louis, George, Louise, and Jeanne.
Georges' intelligence and linguistic abilities served him well when he became the editor of the weekly French-language newspaper Le Progres, founded in 1883 and headquartered on New High Street. Le Progrés was politically independent and so popular with Francophone readers (in spite of strong competition from L'Union Nouvelle) that copies of the newspaper trickled back to France. At least one other French Angeleno, Felix Violé, was inspired to move to Los Angeles after reading a copy of Le Progrés at the home of a relative with friends in California (but we'll get to the Violé family later).
Like so many of his countrymen in Southern California, Georges got into wine and liquor production. In fact, Georges soon had to give up editing Le Progrés because his wine business kept him too busy. His grapes were eventually grown in Glendale, but his Hermitage Winery stood at 207 N. Los Angeles Street, close to the heart of Frenchtown. (And now the site is the unattractive Los Angeles Mall. Doesn't seem like a fair trade, does it?)
He was acting president of the Légion Français for three years, but stepped down in 1895 (he was given the title of honorary president as a token of the Légion's gratitude).
In 1894, at the age of 43, Georges married Marie du Creyd Bremond. Marie was 32 and a fellow French immigrant. They had one child together: Evon.
Georges' real estate holdings had their own challenges. In 1896, he sued the city over a dispute regarding streets in the Mesnager housing tract. Two years later, he was threatened by a trigger-happy tenant, Emil Rombaud, and asked for police protection. The same year, the Le Mesnagers sued a different tenant for damaging a rented vineyard. And Georges' more unusual land holdings included partial ownership of the Ventura County islands of San Nicolas and Anacapa. (If you read Island of the Blue Dolphins in fourth grade, it's a fictionalized account of San Nicolas' last Native American inhabitant, Juana Maria.)
Georges bought a huge parcel of land in what is now Glendale, built a stone barn, and planted grapevines. These days, Deukmejian Wilderness Park preserves the land where the Le Mesnagers grew those grapes.
When Georges' stone barn was damaged by a fire and a flood, his son Louis converted it into a farmhouse. The Le Mesnager family lived in the stone house until 1968.
Georges was so well acquainted with "King of Calabasas" Miguel Leonis that he was one of two executors of Leonis' estate. (Georges made wine and liquor. Leonis liked to drink. What a coincidence.)
The French community held a huge celebration of Bastille Day's centennial on July 14, 1889. Georges Le Mesnager delivered a speech in French at the event.
On September 21, 1892, the French community celebrated the centennial of the French Republic. The celebration - even bigger and more spectacular than Bastille Day's centennial three years earlier - featured Georges as the French-language speaker of the day (this being multicultural LA, someone else gave a speech in English). According to Le Guide Français, published forty years later, "his eloquent and fiery speech still rings in the ears of the older members of the colony."
World War One broke out in 1914. Georges didn't hesitate to return to France and re-enlist in the French Army. He was 64 years old at the time.
Georges didn't even try to negotiate this with his family. It was too important to him. He simply told his oldest son, "Well, my dear Louis, I am leaving for the war. France needs every one of her sons."
Louis objected, "But you are too old to fight."
Georges didn't care. "I promised in 1870 to be there if France were invaded again, and I want to keep my promise."
Georges sent Marie to visit their daughter Louise in Catalina for a week. He asked their youngest daughter, Evon, to gently break the news to her mother when she returned. Marie was very upset, but reasoned "maybe it is all for the best" in a letter to Georges.
So, Georges traveled to New York and set sail for France. As soon as he arrived, he re-enlisted as a private and was assigned to the 106th Infantry.
It wasn't an easy task. French authorities were highly suspicious of anyone entering the country during wartime, and Georges was detained by police at the dock. According to the Ocala Evening Star, a gendarme laughed at his plan to rejoin the army. Georges simply reached into his pocket and took out his prized Legion d'honneur medal - the highest military or civilian honor a French citizen can receive.
"I came from America in 1870 and fought for France and they gave me this. I've come back to fight again."
With the Germans rapidly approaching Paris, soldiers were desperately needed. This was not the time to quibble over a willing volunteer's age. The gendarme kindly directed him to a recruiting station down the street.
The recruiter was hesitant. A 64-year-old private in the infantry was pretty much unheard of. But Georges showed the recruiter his Legion d'honneur medal, and he was on a troop train that very night.
After just seven days on the front, Georges was shot through the arm and hospitalized for a month. He was quickly promoted to sergeant for gallant conduct.
Georges spent months in the trenches at the seemingly endless battle of Verdun. One day, the unthinkable happened: the 106th ran dangerously low on ammunition.
The colonel asked for a volunteer to retrieve more ammunition. It was a suicide mission. But Georges volunteered, and in spite of the German army's best attempts to shoot him down, succeeded. For his courage, he was given the croix de guerre. The colonel told his regiment "Every soldier should have the courage and spirit of this veteran comrade."
One night, Georges was talking to his regimental adjutant when a German artillery shell passed between them, landed nearby, and exploded.
Both men survived, although the explosion sent them flying. Georges regained consciousness under a tree, retrieved parts of the spent artillery shell, brought them back to the trench, and showed them to his troops.
"It was nothing at all, nothing at all," he laughed. "Don't ever be afraid of a shell like this one. It's only the shell that hits you that you need to dread."
The colonel overheard this remark, and recommended Georges for further honors. He received another medal, the palme.
In a later battle, a massive German soldier tried to take out the aging Georges - who ran him through. For this, he received yet another medal, this one for bravery in hand-to-hand combat.
Georges' courage in the battles of Eparges, Chemin des Dames, and the trancheé de Calonne did not escape notice, and he was wounded five times during the war.
Georges' family knew nothing of this until Marie read about his heroics in a book published after the war's end. She told the Tonopah Daily Bonanza "It is characteristic of my husband that he should say nothing of being wounded. He never writes anything about himself. It is always about the bravery of others. The only information of personal nature I had from him was that his weight had decreased, but he always insisted he was well. He did write from a hospital, but stated he was there on business. He might be wounded a dozen times, but he never would tell us about it."
(That article, by the way, was unkindly titled "Old Man Runs Away From Home to Fight." The Ogden Standard also published Marie's comments under a different title.)
In 1916, Georges - now a Sergeant Major - was granted a leave of absence, and returned to Los Angeles. During his leave, he focused his energies on two important tasks: defending France from scapegoating, and raising funds for the wounded and maimed soldiers in his regiment. The French community and its supporters were very generous, and Georges was able to bring a good amount of money back to France when he rejoined his regiment.
Besides medals, Georges' leadership and courage earned him the praise of Generals Foch, Pershing, and de Castelnau. He was also appointed lieutenant flag bearer of the 106th Infantry.
As the war drew closer to an end, Georges - now a Lieutenant - was transferred to special duty under General Pershing. In this role, he acted as a liaison and translator for one of the French army divisions that trained with the American military. He led the Alsatian veterans when the army entered Strasbourg.
Georges told the Ocala Evening Star "I couldn't remain quiet when the war broke out. Ever since 1871 I had itched to get back at the Germans...It was one of the happiest days of my life when the United States, my country, joined in the war against Germany on the side of the country of my birth."
While Georges was away fighting for France, his family founded the Le Mesnager Land and Water Company. They secured partial rights to the Verdugo Wash stream, which supplied water to the vineyard.
Georges returned to Los Angeles after the war ended. After four years of the war to end all wars (need I mention he was 68 when it ended?), he'd earned a well-deserved rest. But he had one thing left to do.
After returning to his home in Echo Park, Georges founded the Section Nivelle des Véterans Français de Los Angeles - a society for LA's French war veterans. He also served as its first president.
Finally, Georges decided it was time to retire. He bought a mansion in the Verdugo Hills called Sans Souci ("without a care" in French), which should not be confused with the Sans Souci fantasy castle in Hollywood.
In 1921, Georges was partially paralyzed by an apoplectic stroke. He knew it was the beginning of the end, and decided to spend his last days in France. The following year, he returned to Mayenne with Marie and Evon. Georges bought another grand property: the Chateau de Kerleón.
At six a.m. on September 6, 1923, Georges stood up and died in his nurse's arms.
Georges was buried with full military honors. Every war veterans' association flew its flag at the funeral. This being small-town France, the funeral was held before the very altar where he had been baptized so many years earlier. Colonel Oblet recorded Georges' considerable military accomplishments on his tombstone.
The Chateau de Kerleón was, tragically, destroyed by Nazi bombing in World War II.
Incredibly, the Le Mesnagers' old stone house is still standing at 3429 Markridge Road in Glendale and is being converted into a nature center. There is also a Mesnagers Street in Los Angeles.
Surviving sites associated with the French community are RARE (as of today, I've mapped FOUR HUNDRED, only a handful of which still exist). And yet, somehow, it doesn't seem like enough.
I, for one, would pay good money to see Georges Le Mesnager's story on the silver screen (and I can't sit through war movies).
*Most sources Anglicize Georges' name to George. Since older resources give his name as Georges, which is the correct form in French anyway, I'm calling him Georges.
Thursday, July 14, 2022
Bastille Day in Old LA
On this day in 1789, the French Revolution began.
I an pretty open about having a complicated relationship with La Fête Nationale/Bastille Day. My dad is a descendant of an earlier French monarch, which makes both Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette my very distant cousins. My mom's family comes from centuries of French peasant stock.
Still, I wish I could take a time machine to Old LA on this day. The French community put on quite a Bastille Day celebration.
In fact, it used to be a pretty big deal in LA.
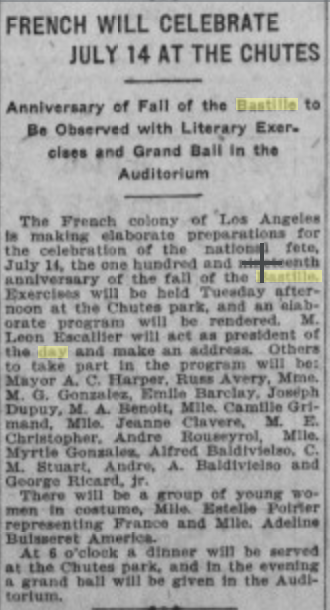
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1881 |
One of the earliest references I can find lists the parade route: Aliso to Arcadia, Main to the Plaza, then to Spring, Spring to Second, Second to Fort (Broadway), Fort to Fourth, Fourth to Main, Main to the junction with Spring, and to the Turnverein Hall for speeches. "A representation of the Bastille" (i.e. a very early parade float) was included in the procession.
This route would have effectively started in the French Colony, gone to the Plaza, doubled back and wound through downtown, ending up where the Convention Center parking lot is today. For comparison, the Rose Parade follows a roughly 5.5 mile route.
Two of the speakers were Pascal Ganée and Georges Le Mesnager, who was quite well known for his speeches! More on that in a minute.
Bastille Day 1881 concluded with a banquet at the Pico House, prepared under one of LA's early celebrity chefs, Victor Dol.
On this day in 1882, the festivities began with a 21-gun salute at sunrise from Fort Hill. The Mayor, the President of the City Council, "delegates from fire companies and civil societies", French citizens of varying prominence, and a beauty queen - the Goddess of Liberty - all made appearances.
The Goddess of Liberty chosen for the event, by the way, happened to be 14-year-old Narcisse Sentous, eldest daughter of Jean Sentous. She was carried in a "Car of Liberty" with several maids of honor, all girls from the French Colony.
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1882 (snippet of much longer article) |
The parade procession was big enough to have two divisions, both made up of prominent citizens and local societies. Besides the Car of Liberty, another car had Marie Deleval representing France, Mathilde Reynaud representing the United States, Honoré Penelon (eight-year-old son of the late Henri Penelon) dressed as the Marquis de Lafayette, and ten-year-old Auguste Lemasne dressed as George Washington. Rounding up the rear were citizens riding donkeys in tribute to the city's butchers.
Eugene Meyer, the "President of the Day" (i.e. Grand Marshal) and then-Agent for the French consulate, gave a speech in French and introduced Frank Howard (who gave a quick history lesson on Bastille Day in English). "The Star-Spangled Banner" was sung, the band played, "La Marseillaise" was sung, and Georges Le Mesnager gave a speech in French.
And that wasn't all. A large model of the Bastille had been built on Fort Hill. After the sun went down, it was stormed and set on fire. (Good thing two fire companies were there!)
The day concluded with a party at Armory Hall.
In 1886, the French Colony invited the editor of the Los Angeles Herald to attend the Bastille Day celebration. He had a prior commitment in Long Beach that day, but thanked the French Colony in the newspaper.
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1886 The newspaper did still cover the event, of course. In spite of a half-hour rainstorm (an extreme rarity during a Southern California summer), the parade went on, although many people who had planned to join the parade waited inside the French Theatre for the rest of the day's events. The President of the Day was Jean-Louis Sainsevain this time - and again, one of the last speeches was given by Georges Le Mesnager. The biggest celebration of them all was held in 1889 - the 100th anniversary of the French Republic. Besides the usual festivities, an extravagant banquet and ball was held at the Pico House, then owned by Pascal Ballade and renamed the National Hotel. The speech Georges Le Mesnager gave on this day was particularly well remembered by French Angelenos - and you can read most of it (thoughtfully translated into English by the Los Angeles Herald) here. |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1891. |
An interesting footnote to the 1891 celebration is that one of the vocalists was J.P. Goytino, who despite having some musical talent was also a highly problematic newspaper editor/slumlord/all-around dirtbag. Goytino is perhaps most notorious for stopping issuance of a marriage license five years later when his extremely wealthy father-in-law, Joseph Mascarel, sought to legally marry his common-law second wife. (He needn't have bothered; Mascarel left most of his fortune to his grandchildren from his first marriage.) I could do a pretty ugly deep dive on Goytino, but David Kimbrough already did a very thorough one on Facebook (warning: it's a 12-parter).
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1900 |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1901 |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1908 |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1908 |
 |
| Hollywood Citizen-News, 1940 |
 |
| Los Angeles Times, 1947 |
After the war, Bastille Day was back - and hosted by the Los Angeles Breakfast Club!
 |
| Los Angeles Daily News, 1949 |
Los Angeles Times, 1951  |
| Los Angeles Times, 1957 |
 |
| Highland Park News-Herald and Journal, 1957 |
 |
| Los Angeles Times, 1960 |
Bastille Day was a big enough event to merit an annual flag ceremony at City Hall and draw a crowd of thousands to the Colony’s celebration. That certainly isn't the case now, and I fully expect Mayor Garcetti to ignore Bastille Day again, as Mayors of Los Angeles have tended to do for years.
Monday, August 14, 2017
We're Still Here, Part 3C: The Le Mesnager Barn
This nature park preserves 702 acres of wilderness, including the Le Mesnager family's former vineyard. (The park was named for then-Governor George Deukmejian, a Glendale native who helped buy the land back from a developer.)
The Le Mesnager family owned and lived in this barn (converted to a farmhouse by Georges' oldest son Louis after fire/flood damage) until the late 1960s. It's conveniently located close to the park's entrance, right next to the parking lot.
What's that in front of the barn?
Grapes! Yes indeed, they're used to make wine.
The barn is right next to this little amphitheater.
Seen from the back.
It's tricky to get a good angle on the barn when you can't get too close.
Don't let the sign fool you - I snapped these pictures in May. The barn's conversion/remodel was still clearly underway.
When the barn is re-opened to the public (and when I have time to drive waaaaaaay out to the furthest edges of the Valley - seriously, getting here took forever), I will be back to take better pictures.
Thursday, March 3, 2022
The Barn is Back!
The Le Mesnager barn, long closed to the public, is finally reopening.
The stone barn, built long ago by Georges Le Mesnager, was converted into a house after it was damaged by a fire and a flood in the 1930s. Members of the Le Mesnager family lived in the converted barn until 1968.
The barn has been adapted into a nature center, and will reopen on March 19.
Thursday, July 13, 2023
Some Forgotten French Papers of Old LA
One of the most annoying aspects of researching French LA is that some historical documents, especially those written in Northern California, either completely ignore the French Colony in LA or - at most - treat it as an afterthought.
A reader pointed me toward the California Historical Society Quarterly's four-part series on the French-language press in California, written by one Clifford H. Bissell. I wasn't optimistic, but I always check these things out just in case. The CHS is known to have an impressive collection of newspapers.
Part one: blah blah blah NorCal.
Part two: blah blah blah more NorCal.
Part three: blah blah blah it's like the southern half of the state doesn't exist.
Part four: blah blah blah NorCal NorCal NorCal...then, long after I'd abandoned hope, a section on the French press in Southern California began on the thirteenth page.
FINALLY.
I've mentioned the Spanish-language newspaper El Clamor Público before. For a brief period of time, the newspaper printed a page in French - not surprising, since editor Francisco P. Ramirez learned French from his godfather Jean-Louis Vignes. After the French page ended its run a few months later, the occasional French-language article, letter, or ad continued to run. This is also not surprising, since many French Angelenos picked up Spanish before (or instead of) English.
Two years after Corsican-born F. Tamiet founded L'Union in 1876, Tamiet disappeared. L'Union's editor F.V.C. de Mondran, who had left to establish Le Courrier de Los Angeles, used its debut issue to explain that Tamiet had forged checks, embezzled money, and left debts behind. The French Benevolent Society's meeting minutes from much of 1877 are missing, possibly because Tamiet was the Society's secretary at the time and may have been destroying unflattering records.
Mayor Joseph Mascarel was the second owner of L'Union. Bissell does insult Mascarel's intelligence, claiming he was nearly illiterate (I have never seen anything to indicate this claim is true).
As for F.V.C. de Mondran, aka Frédéric François, Vicomte Cazeaux de Mondran, his newspaper career seems to have been short-lived, as Le Courrier only lasted a few issues, and he left town soon after that (although unlike Tamiet, he didn't leave any sort of mess behind him and doesn't seem to have had a known reason for leaving).
Pierre Ganée founded weekly paper L'Union Nouvelle in 1879, not long after L'Union folded, and remained editor and publisher until he passed away in 1902. The paper was widely read by most French-speaking families in Southern California, and was still being published when the Herald-Express ran its last issue in 1962.
Le Progrès followed in 1883, helmed by Dr. Pigné-Dupuytren and then Georges Le Mesnager, neither of whom really had the time to both keep it going and attend to their other jobs. For a time, J.P. Goytino, notorious son-in-law of Joseph Mascarel, edited the paper, but he left to focus on the Basque-language Eskual-Herria. (Goytino had a well-earned bad reputation that goes far beyond the scope of this entry. He was particularly notorious for being a scam artist and a slumlord.)
Belgian-born Charles Raskin (whom we've briefly met before) founded Le Gaulois in 1887, but ceased publication in 1891 due to being called to Brussels for his other job (agent for the Red Star Line and Compagnie Générale Transatlantique). Subscribers were turned over to L'Union Nouvelle after the final issue of Le Gaulois. Raskin also used the final issue to call out J.P. Goytino.
Roughly translated:
An unfortunate and miserable vagabond, let's name him, J.P. Goytino, a former resident of the Los Angeles County Prison, has particularly taken on the task of vilifying us. We know full well that he belonged in France, for three years, to the Congregation of the Ignorant Brothers, under the name of Frire Lupulus, and that he was guilty of a series of unnatural crimes. Forced to leave France as a result of these misdeeds - and also as a result of acts of fraud and forgery committed to the detriment of his uncle, Mr. Bernard Etcheverry, he failed in California. Everyone knows that he owes only to the accidental death of his cousin Léonis, not to occupy a cell today in the state prison in San Quentin. It was as a result of his fortuitous release that he became editor of Le Progrés! Our readers know what has been achieved.
Félix Violé came on board at Le Progrés - the very same newspaper that had inspired Félix and his brother Jules to come to Los Angeles - in 1890.
The 1891 city directory lists a Le Progrés Californien, with no editor or publisher listed, and there seem to be no other references to it anywhere. Perhaps it was short-lived, like Le Courrier, but with no surviving copies. That left Le Progrés as L'Union Nouvelle's only serious competition.
Ganée was certainly an opinionated editor. L'Union Nouvelle leaned Democrat until 1896, when Ganée's disapproval of President Cleveland's trade policy prompted him to switch the paper's allegiance to the Republican Party. Bissell adds "It was very anti-British, and seemed obsessed with the likelihood of the world's being dominated by the Anglo-Saxon races, i.e. Great Britain and the United States. It was rabid on the subject of Dreyfus."
(The less said about Ganée's opinion of Alfred Dreyfus, who was wrongly accused, wrongly convicted twice, and the subject of a cover-up when the real traitor was uncovered, the better. Ganée was eventually forced to admit Dreyfus' innocence.)
Ganée was equally mistaken about the Spanish-American war, believing Spain's navy to be superior to that of the United States. Oops!
Jean Trébaol edited Le Progrés either with or under the direction of Goytino, but left after a squabble and founded Le Français. He proudly advertised it in English as "the only French newspaper in Southern California established, owned, and published by a Frenchman." This must have come as news to Pierre Ganée, the Frenchman who established, owned, and published the long-running L'Union Nouvelle. In the end, Le Français merged with L'Union Nouvelle in 1900, and Trébaol went back to his old job: teaching. Like Tamiet, he mysteriously disappeared in 1919, but I'll dig into that another time.
Friday, January 8, 2021
News, Maps, Guns, and Félix Violé
Félix and Jules Violé happened to be visiting their cousin in Bayonne when they encountered something unexpected: a copy of Le Progrés.
Founded in 1883, Le Progrés was one of 19th-century LA's French-language newspapers (there were at least four, and there is some evidence that there may have been as many as ten). Le Progrés was politically independent and a popular newspaper, despite strong competition from rival paper L'Union Nouvelle (which lasted until well into the twentieth century). And a relative in Los Angeles had sent an issue of the newspaper to the Violé brothers' cousin.
A busy frontier city in the furthest reaches of the faraway American West had so many French expats that it had its own French-language newspaper - more than one, in fact. The very idea intrigued both brothers (who had little to look forward to besides modest success and a comparatively dull life). Félix decided to pack up and move to Los Angeles himself. (Jules would follow him to LA within a year. I will cover him in a separate entry.)
Interestingly, immigration records indicate that Félix entered the United States through another great city with French roots - New Orleans. The year was 1888, and Félix was 30 years old.
Félix quickly settled into his adopted city. He was a civil engineer by training, but as the boom of 1887 was over (thus meaning little work for engineers), he took a job with hotelier Pascale Ballade - the very relative who had sent the copy of Le Progrés to Bayonne in the first place. Soon, Félix became editor of a different local French-language newspaper, Le Gaulois, and served on the committee for the Bastille Day centennial celebration.
I've covered the Bastille Day celebration earlier, in my entry on Georges Le Mesnager. In a strange footnote to one of the biggest events Frenchtown ever hosted, there was a dispute over payment of a bill connected to the celebration. Félix was slated to duel with Charles Raskin, then-editor of Le Progrés, over the issue on September 5, 1889. Strangely, about a year later, Félix was listed as editor of Le Progrés (a position he would hold for two years) and Raskin as editor of Le Gaulois in different newspaper articles. I surmise the issue prompting the duel was solved in a nonlethal manner.
Just a few months after the duel, on January 13, 1890, Félix married Hortense Deleval in San Diego. (Hortense's uncle was murder victim Henri Deleval.)
Félix and Hortense had three children - Gabrielle, Marie, and Laurence. Sadly, Gabrielle only lived for 18 months.
Félix also had a wholesale wine and liquor business, along with his house, at 736 S. Spring Street (a block I know well, having been to 721 S. Spring Street, aka California Millinery Supply, plenty of times). Los Angeles did have some restrictions on alcohol sales by the 1890s, and Félix was fined $20 for selling liquor after hours in 1893.
Two years later, Félix applied for a saloon license and was denied. It isn't clear whether this had anything to do with the 1893 fine - or with the French newspapers' strong opposition to the French gangsters who ran many of the saloons and brothels in neighboring Lil Paree. (Beret-tip to David Kimbrough for the clipping.)
Félix also worked as a surveyor, was the city's official draftsman until his death, ran for City Engineer, and incorporated the Félix Violé Map and Address Company. Félix compiled new maps of Los Angeles said to be the most detailed and complete to date, one of which was distributed free of charge through the city's Chamber of Commerce. If you've ever seen a map of Los Angeles produced in the 1900s-1910s (or a real estate directory), it was probably made by Félix.
Félix was active in the Knights of Columbus, and was an avid clarinetist. Laurence Violé also became a civil engineer, sharing office space with his father at 2nd and Main.
Félix passed away in 1924 and is buried at Calvary Cemetery.
Saturday, May 11, 2019
They Paved Frenchtown and Put Up a Parking Lot
- Mayor Joseph Mascarel's adobe house. The Talamontes-Mascarel adobe, built in 1834, was torn down in 1957. The Huntington Library has the only surviving picture of which I'm aware, and I am eternally grateful to them for letting me see it in person. Now it's Olvera Street parking.
- L'Union Nouvelle offices. Los Angeles' most popular French-language newspaper (which was still being published when the Los Angeles Herald-Examiner ran its last edition) had offices at Arcadia and Main Streets for many years. Now Plaza employees park there.
- Viole-Lopizich Pharmacy site. The Viole family served Los Angeles as pharmacists and physicians for many years. Their pharmacy is now a Plaza parking lot.
- Signoret Block. This classy mansard-roofed brick building also housed Chevalier's pharmacy. Part of the same parking lot as the Viole-Lopizich pharmacy site.
- Another Viole-Lopizich Pharmacy site (and residence). Stood several doors down from the previous Viole-Lopizich pharmacy. Part of the same parking lot.
- Oriental Café. Co-owned by Benjamin Flotte, Victor Dol's uncle. Dol later ran the Restaurant Française in the same building. Part of the same parking lot as the Viole-Lopizich pharmacies and Signoret Block.
- Brunswig Annex. Formerly adjoined the Vickrey-Brunswig Building, which survived and houses La Plaza de Cultura y Artes. Again, same parking lot as the Oriental Café building and Viole-Lopizich pharmacies.
- Le Progrés offices. This politically independent weekly French-language newspaper stood on New High Street in the late 19th century...and its offices disappeared for the same Olvera Street parking lot as the Talamontes-Mascarel adobe.
- Sentous Block. Christine Sterling dressed in widow's weeds and hung a black wreath on the main door when this building was condemned. Pio Pico lived in one of the upstairs apartments after losing everything. Like Mayor Mascarel's house a few doors down, it was demolished in 1957 for Olvera Street parking.
- Jean Bernard's brickyard. A motel and private parking facility stand on the site today.
- Former site of Naud's warehouse. Yes, it burned down. But it also gave the neighborhood (Naud Junction) its name. And now it's parking spaces.
- Prudent Beaudry's house/real estate office. Southern California's first large-scale developer (and builder, two-term mayor, and investor) was working from home way back in the 1880s, owning a house/office on New High Street, behind the Brunswig Building. Now the site is part of a Plaza parking lot. (The Beaudry brothers predicted that people would flood into Southern California once the railroad came to town. They were correct...beyond anyone's wildest dreams. Now LA is overcrowded. Oh, the irony.)
- At least one plot owned by Georges Le Mesnager. 1660 N. Main Street, owned by George before he got into wine and liquor production, is now a parking lot for a DWP facility.
- Georges Le Mesnager's Hermitage Winery. 207-209 N. Los Angeles Street, formerly Georges' walled vineyard (Harris Newmark compared it to a European chateau) is now part of the Los Angeles Mall...and its underground parking garage. Doesn't seem like a fair tradeoff, does it?
- The Amestoy Building. Built in 1888 in the same block that is home to City Hall, the three-story building was dubbed the city's "first skyscraper" (even though the Nadeau Hotel was taller) and formerly housed the Los Angeles Supreme Court. The Amestoy building survived the Civic Center's redevelopment in the 1920s/1930s...only to be demolished in 1958 for a City Hall parking lot.
- Original site of Philippe's. The Geffen Contemporary at MOCA, including its adjoining parking lot, stands on the approximate location of Philippe's original (1908-1918) sandwich shop. (It could be worse...the site of Philippe and Arbin Mathieu's previous restaurant currently hosts the city jail.)
- Michel Lachenais' ranch. Okay, Lachenais was a violent convicted murderer. But his former homestead now boasts a Paragon Parking location, so it still makes this list.
- Ducommun Yard. This site has had quite a history of its own! Well within the original boundaries of Frenchtown, it housed Los Angeles' first passenger depot and locomotive roundhouse, and by the 1920s it was a DWP facility (fittingly, Charles Ducommun was one of the DWP's original stockholders). Ducommun Industries operated on the site before moving to South Los Angeles in 1941. The property is currently a large depot and parking facility for buses.
- One of Louis Mesmer's New York Bakery sites. Part of the Ducommun Yard property, on Alameda Street.
- Hotel de Strasbourg. Ducommun Yard on Alameda Street, again.
- M. Sainsevain's feed store. Also part of the Ducommun Yard property.
- Much of El Aliso/Sainsevain Brothers Vineyard. Jean-Louis Vignes' 104-acre property has been divided over and over, so multiple parking lots/garages are on this chunk of land roughly bordered by the Los Angeles River to the west and the 101 Freeway to the north.
- Former Larronde-Etchemendy mansion. The beautiful Victorian mansion at 237 N. Hope St., home to the blended Larronde-Etchemendy family for nearly 80 years, was torn down along with the rest of Old Bunker Hill. The house stood about where the DWP parking lot is today.
- Raymond Alexandre's Roundhouse. LA's earliest known example of fantasy architecture, LA's earliest amusement park, LA's earliest kindergarten...and within the former grounds is a large Paragon Parking lot.
- Ponet Square Hotel. Formerly the largest apartment building in Los Angeles (built 1906), this hotel was torn down in the days immediately following a deadly arson fire in 1970 (which led to a badly needed update to the 1943 fire code) and promptly turned into (what else...) a parking lot. It's been a parking lot ever since.
- Two other portions of Ponet Square itself. Ponet Square includes two additional parking lots, albeit smaller ones.
- Pershing Square. Technically still there, but mostly paved over and altered beyond recognition. This is the worst public park in Southern California, partly because building an underground parking garage and elevating the park to allow for said garage has led to too much concrete and not enough tree shade. Pershing Square can be scorching hot on 60-degree days. The previous design should have been left the hell alone (if it isn't broken, don't "fix" it!). Oh well, at least the Doughboy isn't going anywhere.
- Mesmer Building. Louis Mesmer built a two-story building at the corner of Los Angeles and Requeña Streets, later opening Requeña to Alameda Street. Requeña Street was renamed Market Street and no longer exists. Mesmer's building was replaced by a City Hall parking garage.
- The entire Sentous tract, including the Sentous Street School. Razed in 1969 to build a massive parking lot for the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Staples Center (and its parking garages) now take up much of the land. Sentous Street was renamed L.A. Live Way.
- First Methodist Church. While most French Angelenos were Catholic, Melvina Lapointe Lott - niece of Remi Nadeau - belonged to this church and donated three Tiffany mosaic panels said to be Tiffany's very finest work. The church was razed (for a parking lot, what else) in the 1980s (thankfully, the Tiffany panels now belong to the Lake Merritt United Methodist Church in Oakland). On a personal note, I have used that parking lot many times...and I became very nauseous when I realized I'd repeatedly parked on the former site of a Tiffany masterpiece.
- Germain Pellissier's house. Entire block is now occupied by a hideous multi-level parking facility across the street from the Walt Disney Concert Hall.
- Jean Sentous' dairy farm. The farm, bordered by Grand, Washington, Main, and 21st Streets, changed hands a few times, becoming Chutes Park in 1900. There are now several parking lots and a courthouse parking structure on the land.
- One of Pascale Ballade's saloons. Ballade had a few drinking establishments to his name, and the one at 742 S. Main Street is now a parking lot!
- Remi Nadeau's city block. Nadeau's land holdings included most of the block bordered by Hill, 4th, Broadway, and 5th Streets. His freighting business was headquartered here - corrals, stables, blacksmiths, and a wagon repair shop stood on the land. Today, there are multiple commercial properties, a government office...and two parking lots.
- Louis Mesmer's house. The approximate location of 127 S. Broadway is now the entrance to a courthouse parking garage.
- André Briswalter's home (possibly). Briswalter lived at the corner of Washington Boulevard and Main Street. One of the four corners of the intersection is now a large parking lot.
- Dehail House Hotel. Like all the other French-owned boarding houses in the area, it's long gone. Most would have been too close to the 101 Freeway to survive the 1950s, but this one is - you guessed it - a Little Tokyo parking lot.
- Charles Ducommun's mansion. By 1892, the Ducommuns had moved out, and the house became a boarding house for newsies and other young working boys. It later became a men's boarding house, and finally a boarding house for Japanese tenants. And now the site is a parking facility.
- Victor Dol's house. There's ONE parking lot on this block...and its location corresponds to the talented chef's address.
- Old Calvary Catholic Cemetery. The Diocese of Los Angeles decided the cemetery would better serve its needs as Cathedral High School's parking lot and athletic fields. Numerous Catholic Angelenos, many of them French, had to be re-interred at New Calvary. (Marcelina Leonis' original headstone is installed in the field fence like it's an art piece...as if dying of smallpox at age 20 wasn't bad enough. I, personally, find it disrespectful.)
- City Cemetery. The French Benevolent Society had its own parcel at the cemetery for members. Now it's a parking lot for the Board of Education.
- Champ d'Or Hotel/Taix Restaurant. The Taix family tore down their circa-1882 bakery to build the hotel in 1912. In 1927, Marius Taix Jr. took over the ground-floor restaurant from a tenant. Taix opened its current location in Echo Park in 1962. The 1912 building was torn down in 1964...for a very large parking structure across Alameda Street from the Justice Department and the Metropolitan Detention Center.
- Portions of Germain Pellissier's sheep ranch. It's unclear how much land Pellissier actually owned (sources disagree wildly). However, there are parking facilities adjacent to the Wiltern Theatre, which was built by Pellissier's grandson on land Pellissier had owned (and now my newer readers know why the entire 12-story structure is called the Pellissier Building).
- The Godissart home. Cosmetics mogul Joseph Godissart and his family moved to 810 S. Harvard Boulevard, which has been replaced by an apartment block...with a parking garage.
- Léon Bary's home. French actor/director Léon Bary's home is now an auto body shop...and its parking lot.
- Firmin "Frank" Toulet's house. Frank Toulet, founder of Musso and Frank Grill, was living at 1813 W. 79th Street at the time of his death. Now it's a fenced parking lot behind a commercial property.
- Paul de Longpré's home and gardens. The great painter's roses are long gone, with a parking garage occupying part of the site.
- Various swaths of Victor Ponet's farm. Ponet owned much of modern-day West Hollywood. There are too many parking facilities, public and private, to list.
- L. Giroux's grocery and home. Monsieur Giroux spotted Santa Monica, fell in love with it, and built a combination home/grocery store (Santa Monica's second house, supposedly, after Eugene Aune's). The house is long gone and the land is occupied by Parking Structure 6. (And I thought I'd run out of reasons to hate the Third Street Promenade!)
- Le Mesnager vineyard. As glad as I am that the Le Mesnager family's barn survived (and reopened to the public in 2022), Deukmejian Wilderness Park's parking lot IS uncomfortably close to the buildings. I'm just saying, it *could* have been placed closer to the park's entrance.
Monday, May 30, 2016
Memorial Day Special Edition: The Doughboy
I originally intended to write about people/places/things more or less in order, and had planned to make Jean Louis Vignes the focus of today's entry.
Vignes is far and away one of Frenchtown's most important figures. But he can wait a little longer.
There are three reasons for this:
1. Today is Memorial Day.
2. Pershing Square is getting a major renovation in the near future (from a Paris-based firm, no less).
3. Pershing Square is home to a very important, and widely ignored, war memorial.
As my dear readers will discover in future entries, LA's French community has a history of strong support for both France and the United States in times of war (by the way, can we please retire that stereotype already?). This was especially apparent during World War I.
The 1918 Los Angeles City Directory (i.e. phone book) lists French organizations of support: the French Ambulance Service is listed at the same address as the Alliance Francaise (still active today in a different location), and the French Society for Relief of Wounded Soldiers was just three blocks away. Since phone books tend to be compiled in advance, these organizations were likely founded in or before 1917, when the US entered World War I.
France's busiest supporter in Los Angeles at the time was very likely Lucien Napoleon Brunswig (who will get his own entry later). Born in Montmedy, France, Brunswig moved to Los Angeles in 1903 and founded a very successful pharmaceutical company. He then went on to become the busiest pharmacist in the city's 234 years of history.
Besides running LA's largest wholesale medicinal supplier, Brunswig served as president of the Alliance Francaise, founded the Cercle Catholique Francaise (which aided new immigrants from France), and was active in the California State Society. During the war, his efforts included the American Committee for Devastated France and the Maisons-Claires (which supported 64 war orphans in Trinity-sur-Mer, France).
Brunswig took his efforts a step further by returning to war-torn France in 1917, spending eight months in the country and writing about the experience, in spite of being 63 years old. (Another French Angeleno, Georges Le Mesnager, juggled four jobs - vineyard owner, court translator, notary, and editor of the Francophone newspaper Le Progrés - and stepped away to fight for France in World War I. He was 64 at the time - too old to be an officer - so he re-enlisted as a private. Le Mesnager later acted as a French army liaison to Gen. Pershing himself.)
In 1923, the Soldier Monument Committee of the Association of the Army of the United States was founded, with the goal of raising funds to erect a memorial to Los Angeles residents who had died in World War I. Lucien Brunswig served as vice chair of the Committee.
The statue, known as "The Doughboy", was commissioned from sculptor Humberto Pedretti and dedicated July 4, 1924, in Pershing Square (renamed in 1918; originally Los Angeles Park).
In 1927, the French Veterans of the World War added to the statue, giving it a bronze relief of a French helmet and an olive branch. Photos of the Doughboy (and the relief) can be seen here.
For his considerable efforts, Brunswig was awarded the Legion d'Honneur - France's highest order for both civil and military merits. Sadly, Brunswig did not live to see the Allied victory in World War II; he passed away in 1943.
I am not now, nor will I ever be, in the military. But I am a firm believer in showing appreciation for those who put themselves in harm's way to keep the rest of us safe.
Pershing Square has been widely disliked for quite some time now - not enough shade, not inviting, etc. I have seen Agence Ter's concept artwork for redeveloping the park, and I think it's going to be stunning.
But I am worried about the fate of the Doughboy.
In 1924, the Doughboy was installed at the park's northwest corner, meant to be its gateway work of art. Currently, it stands in the Palm Court.
Few modern-day Angelenos have any idea the statue is even there. I suspect the number who have taken the time to appreciate it is even lower. My dad, who attended USC and worked downtown for well over a decade, didn't know the Doughboy existed until I told him about it. My grandfather, a French-American war veteran (specifically, a tank commander in France under Patton) and a vocal believer in supporting other veterans, probably only saw it on a onetime visit to Pershing Square (which, to a family living in then-suburban Santa Monica, was a pretty scary neighborhood at the time).
Throw in the fact that horrible people like to vandalize war memorials, throw in the fact that irreplaceable works of art are too often destroyed on purpose, and add the fact that too many Angelenos know nothing about the city's frequently-erased history and don't care enough to learn about it.
I am very worried that the Doughboy won't survive the redevelopment of Pershing Square. And if any work of art should be in a park renamed for Gen. John J. Pershing, it's the Doughboy - a 92-year-old monument to the Angelenos who lost their lives in a terrible war. (Agence Ter's plans include a "sculptural promenade", but I have yet to see anything specific about the Doughboy.)
I will be unable to pay the Doughboy a visit today, as I must go to work and won't have time to go downtown. But if you can make it, leave a red poppy at the statue's base for me.
Incidentally, Remi Nadeau - one of the most important Angelenos you've never heard of (he will get a VERY long entry later) - lived across the street from Pershing Square. The Biltmore Hotel was built on the site of his former home. And to make things even more interesting...the land was part of the Bellevue Terrace tract, developed by French-Canadian mayor/entrpreneur Prudent Beaudry in the 1860s.
P.S. The former Alliance Francaise/French Ambulance Service building was replaced by the United Artists Theater, built in 1927. The site is currently Ace Hotel's Los Angeles location.
Sunday, November 19, 2023
Jean Trébaol Vanishes
Sometimes, people just disappear.
It's much less common in the digital age. It would have been relatively easy to vanish without a trace - either intentionally or unintentionally - in 1919, when Jean Trébaol was last seen alive.
Born in Brest, he came to the States in 1893 at the age of 24, and soon married another Brest native, Jeanne de Kersauson de Pennendreff. The couple rented a house at 125 4th Street and would eventually have fourteen children (with thirteen surviving infancy).
Jean was a teacher and linguist, but took a job editing the French-language newspaper Le Progrès either with or under the notoriously unsavory J.P. Goytino. A squabble prompted Jean to leave and establish his own paper, Le Français. He boasted in English-language advertisements that Le Français was "the only French newspaper in Southern California established, published, and owned by a Frenchman."
This must have come as quite a surprise to Pierre Ganée, a fellow French immigrant who established, published, and owned rival paper L'Union Nouvelle.
The Herald published an article in 1897 about Constance Goytino (wife of J.P. and daughter of Joseph Mascarel) horse-whipping Mme. Trébaol outside a courtroom after a hearing. Jeanne's 17-year-old brother Robert, who was to inherit a considerable sum of money, had nominated J.P. as his legal guardian. Jeanne and her sister Isabel had concerns about Goytino's appointment. Constance also accused the Trébaols of trash-talking her. Jean sent a letter to the Herald politely informing them that Constance had attacked Jeanne unprovoked, that Jeanne had not actually taken the stand, and that "Judge Clark granted what we were intending for, namely, that Goytino as a guardian be put under heavy bonds and be restrained from incurring any liabilities on the principal of his ward."
Le Français merged with L'Union Nouvelle in 1900, and Jean went back to teaching.
With a large family to support and teacher pay being less than robust, Jean had more than one job. He taught French at Los Angeles High School, taught night classes at Polytechnic High School, taught at the Ebell Club of Pasadena, and taught privately.
He also wrote for the Herald occasionally. Of particular note is Jean's 1901 essay "The Corset Question". While Jean wasn't 100 percent correct on the history of corsets, he expressed concerns over the health effects of tightlacing and predicted - correctly - that some women would continue to wear body-shaping undergarments (although these days waist trainers and other shapewear are far more common than corsets) instead of embracing their natural shape. While he chalks this up to vanity, I surmise he was unaware of the pressure to look a certain way that many women still face, well over a century later.
In 1903, Jean suffered a breakdown from stress, overwork, and starving himself for months to feed his children. He was sent to the San Gabriel sanitarium for a few weeks to recover. A newspaper blurb solicited financial assistance for the Trébaols, who had five children by this point. (Given the date of the article and the birthdates of their children, Jeanne would have been caring for 8-month-old Yvonne and was already expecting Edouard.)
 |
| 1903 blurb regarding Jean Trébaol's hospitalization due to a breakdown |
 |
| Blurb regarding a subscription, or donation fund, for the Trébaols |
Jeanne was appointed legal guardian to her husband after his breakdown. A real estate transaction listed in the newspaper suggests she sold the family home on his behalf.
 |
| 1909 newspaper blurb mentioning Trébaol's second hospitalization |
A snippet from one of the San Francisco papers indicates that Jean lost or pawned a bag filled with important papers and photographs (which were an expensive luxury in 1909) prior to being committed to a mental hospital again. Jeanne came to San Francisco and requested police assistance in locating the bag.
When World War One broke out in 1914, Jean tried to enlist. He was turned down due to being in his forties and having thirteen living children. (Georges Le Mesnager, by contrast, had five children, four of whom had reached adulthood.)
The Trébaols moved to Hollywood, which was still semi-rural. The family's three cows got out one day, prompting the judge to order Trébaol to keep them in another neighborhood and secure them properly.
 |
| 1917 blurb about the Trébaol family's cows escaping |
Jean took a job at the French Consulate for a while, then accepted a teaching post at the Mare Island YMCA in Vallejo, teaching French to sailors from the naval base bound for France. He published a small textbook related to this post. The rest of the Trébaols remained in the family home in Los Angeles.
Jean was known to the staff of the Echo de l'Ouest, one of the Bay Area's own French-language newspapers. He stopped by the newspaper's office on May 31, 1919, appearing to be severely depressed, and told the staff that he needed a complete rest. According to them, he was not himself that day.
On June 1, Jean spent the night at the home of his brother René, who lived in Vallejo. The San Francisco Call stated that he was suffering from a nervous breakdown. He vanished the following morning.
Jean Trébaol was never seen again.
One colleague noted that there was talk of him drowning, which is certainly plausible given Vallejo's location on the Bay. It was widely assumed that he must have died in either an accident or - especially in the light of his apparent depression - by suicide.
Jean never found out that he had just been selected as the Vallejo schools' French teacher.
Jeanne came up from Los Angeles to search for her missing husband, but it was to no avail.
The California Historical Society Quarterly claimed that "Mascarel offered Madame Trébaol a house of prostitution as a good source of revenue after her husband's disappearance, but she declined, especially as she would have to live in it herself!" While the French Colony was known to step up for those in need, this story isn't even possible; Joseph Mascarel had passed away twenty years earlier in 1899 at the age of 83.
Jeanne DID need money, of course. She was a mother of thirteen living children, and although her two oldest children were in their twenties, the youngest was only four years old.
Six of the Trébaol children were already "appearing in motion pictures", as the Call put it, when their father disappeared. The other seven were soon looking for acting gigs as well.
Jean had suffered from memory loss during previous mental health episodes, and had once spotted a newspaper advertisement placed by Jeanne, recovered his memory, and returned home. Besides earning money in the movies, the family hoped Jean would see and recognize one of his children on the screen.
Older brothers Hervé and Oliver went overseas (presumably to fight in the war), returning in 1919 and going on to higher education (in Hervé's case, becoming a priest and serving for years at St. Mariana in Pico Rivera). Eldest daughter Cecile helped Jeanne keep house and worked as a telephone operator at night. The other ten siblings continued to act.
 |
| 1919 news article with picture of Jean Trébaol |
When he was cast as the Artful Dodger in the 1922 version of Oliver Twist, Edouard told the San Bernardino Sun that "somebody asked mother to try to get some of us in the movies and so finally mother took a few of us around to picture studios. It was hard work, walking from studio to studio, and there was very little for us then. In fact it was many weeks before we received our first call. That was for a picture with Miss Pickford. Since then, the picture directors have been very kind. After they learned about our dad...they seemed glad to give any of us work when they could. Now every one of us is in pictures. Why, even mother herself sometimes plays."
 |
| 1922 picture of Jeanne with her 13 children. Headline reads "Thirteen Children Act in Movies But Want Their Daddy Not Fame." |
Out of the thirteen Trébaol children, IMDB lists acting credits for Edouard, Jeanette, François (credited as "Francis"), Philippe, Yves, and Marie. I hasten to add that in the very early days of the motion picture industry, actors were not always credited by name, and it's likely that the other children worked as extras or in uncredited roles, since Jeanne did.
In an interesting footnote, Jeanette was apparently not put off teaching by her father's struggles. A 1946 news article mentions her joining the summer school staff at San Pedro High School thirty years earlier, teaching English and Spanish. That fall, she stayed on, teaching at Polytechnic High during the day and night school in the evenings.
















