Tales from Los Angeles’ lost French quarter and Southern California’s forgotten French community.
Saturday, November 8, 2025
Immediate Demolition Threat to the French Hospital
Monday, July 11, 2022
Prudent Street in Maps
Beaudry Street, named for the Beaudry brothers, still exists.
Victor Street, named for Victor Beaudry, still exists (although it was bisected by the 101 long ago).
Victor Heights, also named for Victor, still exists (although it tends to get lumped in with Echo Park).
There is no street named for Prudent Beaudry specifically.
Anymore, that is. There was a Prudent Street!
 |
| 1894 Sanborn map showing Prudent Street |
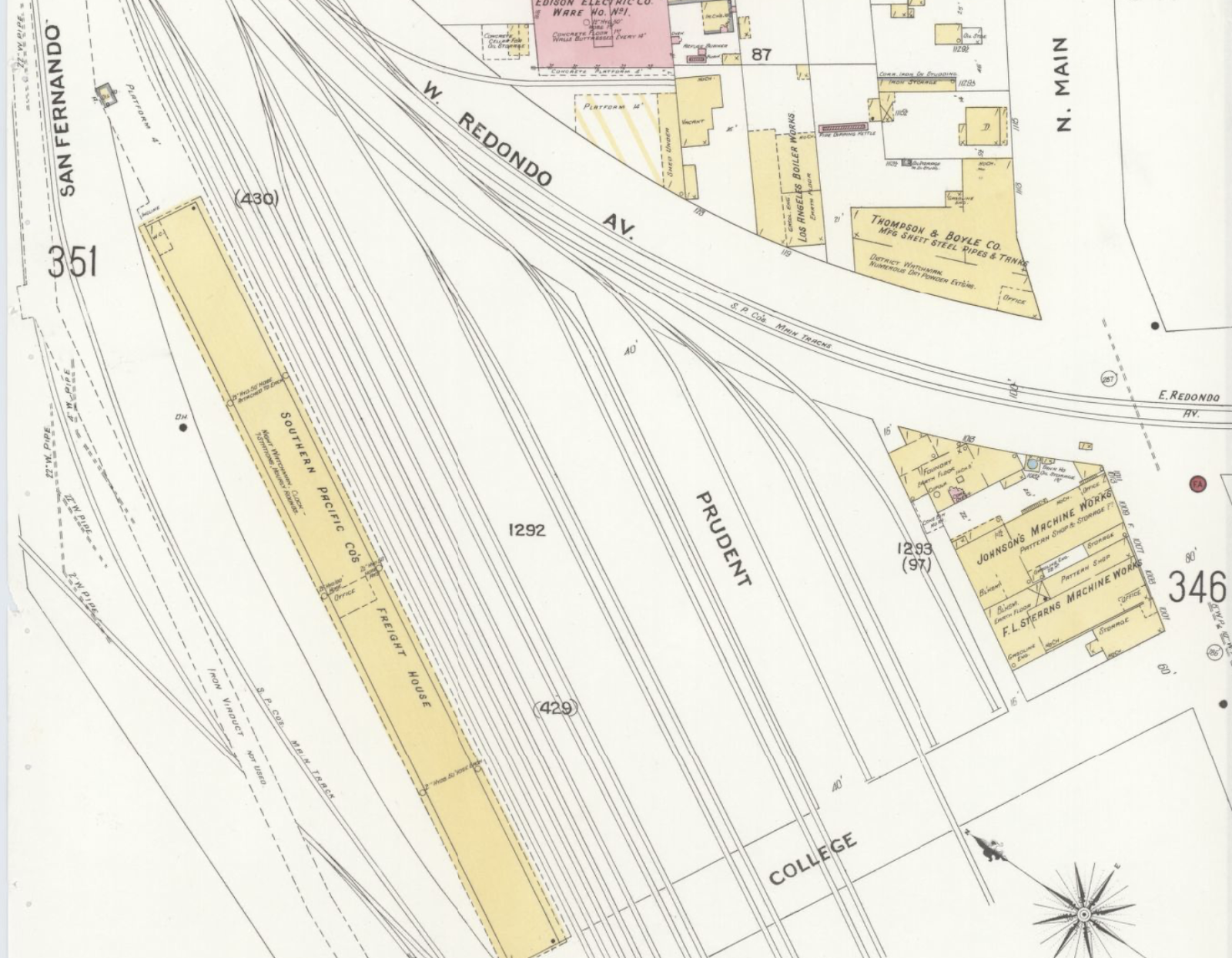 |
| 1906 Sanborn map showing Prudent Street |
 |
| 1920 Sanborn map key detail showing Prudent Street |
 |
| Sanborn map revised 1923, showing Prudent Street Sanborn Map republished 1953, still showing Prudent Street |
A 1950 atlas page that is unfortunately too blurry to post here indicates that Prudent Street was close to Naud Junction, the Bauchet Tract, and the elusive (because the street grid is gone) Ballesteros Tract.
Sunday, January 16, 2022
Little Houses on Bernard Street
Bernard Street is in Chinatown. That is, the short block of Bernard Street that concerns today's entry is in Chinatown.
Bisected by the 110, Bernard has another short block in Elysian Park, and lends its name to an angled extension of Yale Street (shades of Bauchet Street). Many years ago, this was Jean Bernard's brickyard, which he subdivided into the Bernard Tract.
It's quiet in this upper corner of Chinatown. Despite its proximity to both Chinatown Central Plaza and Cathedral High School, the only sound is the soft whooshing of cars - on one end, getting on or off the 110; on the other, driving up or down Broadway. On the south side of Bernard Street, the neon-trimmed Royal Pagoda Motel (reportedly closed at the time of writing) reassures you that yes, you're still in Chinatown and didn't wander into a time warp. This is the side of Bernard that made a cameo appearance in "La La Land" - probably the only time most Angelenos have ever seen Bernard Street.
Sitting in the dark watching the film for the first time, I crossed my fingers, silently begging for the camera to pan to the north side of the street to show the little houses. It didn't.
"La La Land", which shows an incredible (if geographically improbable) checklist of locations in Los Angeles County, didn't show viewers the little houses on Bernard Street. But I will.
 |
| Fritz Houses on Bernard Street |
 |
| Angels Walk stanchion with photo of Louise Fritz Whiting |
 |
| Angels Walk stanchion with picture of 411 Bernard Street |
 |
| Chinese Historical Society at 411 Bernard Street |
Wednesday, September 25, 2019
The French Hospital Will Rise Again
 |
| Demolition fencing at the French Hospital. Photo courtesy of Esotouric. |
Monday, June 17, 2019
Get On the Bus! Preservation Tour September 7
The next three days were a panicked blur.
An overlooked statue, with no landmark status (really, no protection of any kind), wordlessly removed from the privately-owned grounds of a defunct hospital in a city that allows so much of its history to be thrown in the garbage. It didn't look good for poor Jeanne.
And what of the French Benevolent Society, owners of the hospital site since 1869, who haven't had a public presence since 1989 and have yet to make any sort of comment on the sale of the property?
Get the story, straight from yours truly, on Esotouric's inaugural Saving Los Angeles Landmarks tour on Saturday, September 7.
Think you've read it all here? If you still need convincing...
Steve Luftman will be discussing Lytton Savings, Alan Hess will be discussing Pereira's Metropolitan Water District, and although artist Sheila Klein is unfortunately not able to appear, the fate of Vermonica will be featured.
These tours sell out, so get your tickets early!
Saturday, May 11, 2019
They Paved Frenchtown and Put Up a Parking Lot
- Mayor Joseph Mascarel's adobe house. The Talamontes-Mascarel adobe, built in 1834, was torn down in 1957. The Huntington Library has the only surviving picture of which I'm aware, and I am eternally grateful to them for letting me see it in person. Now it's Olvera Street parking.
- L'Union Nouvelle offices. Los Angeles' most popular French-language newspaper (which was still being published when the Los Angeles Herald-Examiner ran its last edition) had offices at Arcadia and Main Streets for many years. Now Plaza employees park there.
- Viole-Lopizich Pharmacy site. The Viole family served Los Angeles as pharmacists and physicians for many years. Their pharmacy is now a Plaza parking lot.
- Signoret Block. This classy mansard-roofed brick building also housed Chevalier's pharmacy. Part of the same parking lot as the Viole-Lopizich pharmacy site.
- Another Viole-Lopizich Pharmacy site (and residence). Stood several doors down from the previous Viole-Lopizich pharmacy. Part of the same parking lot.
- Oriental Café. Co-owned by Benjamin Flotte, Victor Dol's uncle. Dol later ran the Restaurant Française in the same building. Part of the same parking lot as the Viole-Lopizich pharmacies and Signoret Block.
- Brunswig Annex. Formerly adjoined the Vickrey-Brunswig Building, which survived and houses La Plaza de Cultura y Artes. Again, same parking lot as the Oriental Café building and Viole-Lopizich pharmacies.
- Le Progrés offices. This politically independent weekly French-language newspaper stood on New High Street in the late 19th century...and its offices disappeared for the same Olvera Street parking lot as the Talamontes-Mascarel adobe.
- Sentous Block. Christine Sterling dressed in widow's weeds and hung a black wreath on the main door when this building was condemned. Pio Pico lived in one of the upstairs apartments after losing everything. Like Mayor Mascarel's house a few doors down, it was demolished in 1957 for Olvera Street parking.
- Jean Bernard's brickyard. A motel and private parking facility stand on the site today.
- Former site of Naud's warehouse. Yes, it burned down. But it also gave the neighborhood (Naud Junction) its name. And now it's parking spaces.
- Prudent Beaudry's house/real estate office. Southern California's first large-scale developer (and builder, two-term mayor, and investor) was working from home way back in the 1880s, owning a house/office on New High Street, behind the Brunswig Building. Now the site is part of a Plaza parking lot. (The Beaudry brothers predicted that people would flood into Southern California once the railroad came to town. They were correct...beyond anyone's wildest dreams. Now LA is overcrowded. Oh, the irony.)
- At least one plot owned by Georges Le Mesnager. 1660 N. Main Street, owned by George before he got into wine and liquor production, is now a parking lot for a DWP facility.
- Georges Le Mesnager's Hermitage Winery. 207-209 N. Los Angeles Street, formerly Georges' walled vineyard (Harris Newmark compared it to a European chateau) is now part of the Los Angeles Mall...and its underground parking garage. Doesn't seem like a fair tradeoff, does it?
- The Amestoy Building. Built in 1888 in the same block that is home to City Hall, the three-story building was dubbed the city's "first skyscraper" (even though the Nadeau Hotel was taller) and formerly housed the Los Angeles Supreme Court. The Amestoy building survived the Civic Center's redevelopment in the 1920s/1930s...only to be demolished in 1958 for a City Hall parking lot.
- Original site of Philippe's. The Geffen Contemporary at MOCA, including its adjoining parking lot, stands on the approximate location of Philippe's original (1908-1918) sandwich shop. (It could be worse...the site of Philippe and Arbin Mathieu's previous restaurant currently hosts the city jail.)
- Michel Lachenais' ranch. Okay, Lachenais was a violent convicted murderer. But his former homestead now boasts a Paragon Parking location, so it still makes this list.
- Ducommun Yard. This site has had quite a history of its own! Well within the original boundaries of Frenchtown, it housed Los Angeles' first passenger depot and locomotive roundhouse, and by the 1920s it was a DWP facility (fittingly, Charles Ducommun was one of the DWP's original stockholders). Ducommun Industries operated on the site before moving to South Los Angeles in 1941. The property is currently a large depot and parking facility for buses.
- One of Louis Mesmer's New York Bakery sites. Part of the Ducommun Yard property, on Alameda Street.
- Hotel de Strasbourg. Ducommun Yard on Alameda Street, again.
- M. Sainsevain's feed store. Also part of the Ducommun Yard property.
- Much of El Aliso/Sainsevain Brothers Vineyard. Jean-Louis Vignes' 104-acre property has been divided over and over, so multiple parking lots/garages are on this chunk of land roughly bordered by the Los Angeles River to the west and the 101 Freeway to the north.
- Former Larronde-Etchemendy mansion. The beautiful Victorian mansion at 237 N. Hope St., home to the blended Larronde-Etchemendy family for nearly 80 years, was torn down along with the rest of Old Bunker Hill. The house stood about where the DWP parking lot is today.
- Raymond Alexandre's Roundhouse. LA's earliest known example of fantasy architecture, LA's earliest amusement park, LA's earliest kindergarten...and within the former grounds is a large Paragon Parking lot.
- Ponet Square Hotel. Formerly the largest apartment building in Los Angeles (built 1906), this hotel was torn down in the days immediately following a deadly arson fire in 1970 (which led to a badly needed update to the 1943 fire code) and promptly turned into (what else...) a parking lot. It's been a parking lot ever since.
- Two other portions of Ponet Square itself. Ponet Square includes two additional parking lots, albeit smaller ones.
- Pershing Square. Technically still there, but mostly paved over and altered beyond recognition. This is the worst public park in Southern California, partly because building an underground parking garage and elevating the park to allow for said garage has led to too much concrete and not enough tree shade. Pershing Square can be scorching hot on 60-degree days. The previous design should have been left the hell alone (if it isn't broken, don't "fix" it!). Oh well, at least the Doughboy isn't going anywhere.
- Mesmer Building. Louis Mesmer built a two-story building at the corner of Los Angeles and Requeña Streets, later opening Requeña to Alameda Street. Requeña Street was renamed Market Street and no longer exists. Mesmer's building was replaced by a City Hall parking garage.
- The entire Sentous tract, including the Sentous Street School. Razed in 1969 to build a massive parking lot for the Los Angeles Convention Center. The Staples Center (and its parking garages) now take up much of the land. Sentous Street was renamed L.A. Live Way.
- First Methodist Church. While most French Angelenos were Catholic, Melvina Lapointe Lott - niece of Remi Nadeau - belonged to this church and donated three Tiffany mosaic panels said to be Tiffany's very finest work. The church was razed (for a parking lot, what else) in the 1980s (thankfully, the Tiffany panels now belong to the Lake Merritt United Methodist Church in Oakland). On a personal note, I have used that parking lot many times...and I became very nauseous when I realized I'd repeatedly parked on the former site of a Tiffany masterpiece.
- Germain Pellissier's house. Entire block is now occupied by a hideous multi-level parking facility across the street from the Walt Disney Concert Hall.
- Jean Sentous' dairy farm. The farm, bordered by Grand, Washington, Main, and 21st Streets, changed hands a few times, becoming Chutes Park in 1900. There are now several parking lots and a courthouse parking structure on the land.
- One of Pascale Ballade's saloons. Ballade had a few drinking establishments to his name, and the one at 742 S. Main Street is now a parking lot!
- Remi Nadeau's city block. Nadeau's land holdings included most of the block bordered by Hill, 4th, Broadway, and 5th Streets. His freighting business was headquartered here - corrals, stables, blacksmiths, and a wagon repair shop stood on the land. Today, there are multiple commercial properties, a government office...and two parking lots.
- Louis Mesmer's house. The approximate location of 127 S. Broadway is now the entrance to a courthouse parking garage.
- André Briswalter's home (possibly). Briswalter lived at the corner of Washington Boulevard and Main Street. One of the four corners of the intersection is now a large parking lot.
- Dehail House Hotel. Like all the other French-owned boarding houses in the area, it's long gone. Most would have been too close to the 101 Freeway to survive the 1950s, but this one is - you guessed it - a Little Tokyo parking lot.
- Charles Ducommun's mansion. By 1892, the Ducommuns had moved out, and the house became a boarding house for newsies and other young working boys. It later became a men's boarding house, and finally a boarding house for Japanese tenants. And now the site is a parking facility.
- Victor Dol's house. There's ONE parking lot on this block...and its location corresponds to the talented chef's address.
- Old Calvary Catholic Cemetery. The Diocese of Los Angeles decided the cemetery would better serve its needs as Cathedral High School's parking lot and athletic fields. Numerous Catholic Angelenos, many of them French, had to be re-interred at New Calvary. (Marcelina Leonis' original headstone is installed in the field fence like it's an art piece...as if dying of smallpox at age 20 wasn't bad enough. I, personally, find it disrespectful.)
- City Cemetery. The French Benevolent Society had its own parcel at the cemetery for members. Now it's a parking lot for the Board of Education.
- Champ d'Or Hotel/Taix Restaurant. The Taix family tore down their circa-1882 bakery to build the hotel in 1912. In 1927, Marius Taix Jr. took over the ground-floor restaurant from a tenant. Taix opened its current location in Echo Park in 1962. The 1912 building was torn down in 1964...for a very large parking structure across Alameda Street from the Justice Department and the Metropolitan Detention Center.
- Portions of Germain Pellissier's sheep ranch. It's unclear how much land Pellissier actually owned (sources disagree wildly). However, there are parking facilities adjacent to the Wiltern Theatre, which was built by Pellissier's grandson on land Pellissier had owned (and now my newer readers know why the entire 12-story structure is called the Pellissier Building).
- The Godissart home. Cosmetics mogul Joseph Godissart and his family moved to 810 S. Harvard Boulevard, which has been replaced by an apartment block...with a parking garage.
- Léon Bary's home. French actor/director Léon Bary's home is now an auto body shop...and its parking lot.
- Firmin "Frank" Toulet's house. Frank Toulet, founder of Musso and Frank Grill, was living at 1813 W. 79th Street at the time of his death. Now it's a fenced parking lot behind a commercial property.
- Paul de Longpré's home and gardens. The great painter's roses are long gone, with a parking garage occupying part of the site.
- Various swaths of Victor Ponet's farm. Ponet owned much of modern-day West Hollywood. There are too many parking facilities, public and private, to list.
- L. Giroux's grocery and home. Monsieur Giroux spotted Santa Monica, fell in love with it, and built a combination home/grocery store (Santa Monica's second house, supposedly, after Eugene Aune's). The house is long gone and the land is occupied by Parking Structure 6. (And I thought I'd run out of reasons to hate the Third Street Promenade!)
- Le Mesnager vineyard. As glad as I am that the Le Mesnager family's barn survived (and reopened to the public in 2022), Deukmejian Wilderness Park's parking lot IS uncomfortably close to the buildings. I'm just saying, it *could* have been placed closer to the park's entrance.
Tuesday, January 22, 2019
Watch My LAVA Sunday Salon!
Thursday, July 26, 2018
Hang In There, Joan*
A couple of days ago, I reported that the Jeanne d'Arc statue that has stood outside the French Hospital since 1964 had been removed.
An overlooked statue without any historic/cultural monument status, representing a little-known, largely-vanished community, outside a defunct hospital facility. Those are not promising odds. Those are especially not promising odds in Los Angeles, which is notorious for eating its own history on a regular basis.
Would poor Jeanne end up in a scrap heap? Would she be dumped and forgotten in a cavernous warehouse like the one at the end of Raiders of the Lost Ark? For three days, I couldn't stop worrying about her.
I am relieved to report that although Jeanne has been removed from the site she occupied for 54 years, she is safe.
Some of the information I have requested is very likely to take at least a couple of weeks to make its way to me. But I'll share what I do know.
The French Benevolent Society, which retained ownership of the land underneath the hospital when it became Pacific Alliance Medical Center, recently sold the entire site.** Presumably, the new owners had no use for Jeanne.
I reached out to the FBS' representative in the sale. I was told that the statue had been donated to Children's Hospital.
I contacted Children's Hospital to confirm this. They don't yet have any plans for Jeanne, but did confirm that they have the statue and will keep me posted.
Hang in there, Jeanne. We'll see you again, old friend.
*Yes, that was a Frozen reference. My blog, my rules.
**The FBS paid $5,000 for the hospital site (four lots totaling 2.5 acres) in 1869. The site sold for $33 MILLION. I heard Chinatown property values were higher than ever, but still...wow!
Friday, July 20, 2018
Where Is Jeanne d'Arc? Où Est Jeanne d'Arc?
Missing:
One French national hero. Female, age 54. Approximately 10 feet tall including the base. Last seen in front of the former French Hospital in Los Angeles.
This blog began when I found a seemingly out-of-place statue of Jeanne d'Arc on Google Maps while searching for a long-lost Chinatown restaurant.
The French Hospital was the first of well over 400 French-associated sites I have plotted on a Google map. Jeanne d'Arc has stood guard outside since July 1964. This blog would not exist without her.
And now she is missing.
Regular reader Jérome reached out to let me know about Jeanne's disappearance. I don't go downtown very often, so I have no idea when she vanished.
When the French Benevolent Society sold the hospital building in 1989, it retained ownership of the land on which the hospital sits. I found a mailing address for them, although I don't know how current it is, and I have sent them a letter. Hopefully it's the right address and hopefully they respond.
Someone, somewhere, knows where she is. If you are that person, PLEASE TELL ME. If you know anything at all, PLEASE TELL ME. Comment below, or email losfrangeles at gmail dot com. I can't stand the thought of Jeanne vanishing forever. She was one of the last remaining scraps of Frenchtown and now she's disappeared too.
FRANÇAIS
Saturday, June 9, 2018
A Brief History of Philippe Mathieu and the French Dip
 |
| Neon blade sign at Philippe the Original. |
After a stint owning a deli on Alameda, Philippe and his brother Arbin opened the New Poodle Dog restaurant on Spring Street in 1911 (if it existed today, it would be just southwest of City Hall). The name was likely a tongue-in-cheek reference to the Old Poodle Dog restaurant in San Francisco. The New Poodle Dog closed in 1913, and the Mathieu brothers opened another white-tablecloth restaurant on Alameda Street just south of Aliso Street - the heart of Frenchtown.
Frenchtown had more than a few nicer French restaurants, however, and Philippe had a talent for simpler, but still well-prepared, food. Philippe opened his namesake restaurant on Alameda Street, south of Temple, in 1908. If it existed today, it would be firmly in the middle of Little Tokyo, but at the time, it was the center of Frenchtown's original core.
Philippe's customers often referred to him as "Frenchy", and took to calling the restaurant "Frenchy's".
You know where this is going, right?
Philippe moved his eatery to 246 Aliso Street (south of Los Angeles Street) in 1918 (again, still in Frenchtown's original footprint). That year, he began serving the sandwich we now call the French Dip.
The story of how the sandwich came to be invented varies, depending on who told it and when. I won't rehash any of the origin stories here, but I will refer you to Eater LA's commentary on a Thrillist piece examining who really invented the French Dip. (Read both. Trust me.)
I'll add a little food for thought (pun intended) to both publications' conclusions (spoiler alert: the evidence gives Philippe's a stronger and far more logical claim): imitators typically pale in comparison to originators. Every so often, someone (food blogger, local magazine, travel writer) will sample both, or ask local eaters for their pick of the two French Dips. Philippe's always wins taste tests easily and always wins polls by a landslide.
By the way, I have no personal stake in this and can't offer a firsthand opinion on either version of the sandwich (I don't eat meat). I do, however, believe in giving credit where credit is due.
Philippe packed up and moved up the street (to 364 Aliso) in 1925. But he, personally, didn't stay for very long.
Philippe (whose grandson described him to the LA Times as frugal) had promised his wife that he'd retire when he turned 50. He did indeed retire in 1927 at age 50, selling the restaurant to the Martin brothers and moving back to France with his wife.
But the restaurant, by far one of the very oldest in Los Angeles, had one more move to make. Freeway construction forced Philippe's to relocate to its present location, just north of Union Station on the southern edge of Chinatown.
Los Angeles Magazine recently explored how to correctly pronounce the restaurant's name. What they don't seem to notice is that pronunciation seems to vary based on the speaker's background. Philippe's grandson uses the French pronunciation (no surprise here), and Emeril Lagasse isn't TOO far off. Most Angelenos who didn't grow up speaking French use the Hispanicized pronunciation "Felipe's".
It's worth noting, of course, that many early Angelenos adopted, or at least sometimes used, Spanish versions of their names. To give just a few examples from Frenchtown: Louis Bauchet was typically listed in records as Luis, Jean-Louis Vignes was "Don Luis del Aliso", Pierre Sainsevain was commonly referred to as "Don Pedro", and Henri Penelon was often called "Horacio" or "Honore". Mispronouncing "Philippe" as "Felipe" is, in a way, fitting for one of LA's oldest restaurants.
(In the interest of full disclosure, my parents used to go to Philippe the Original on dates.)
Saturday, May 12, 2018
How I Fell Down The Rabbit Hole to Frenchtown
In the spring of 2013, I was doing two things at once. My mom knew very little about her late father's family, apart from the fact that they were mostly farmers and of French extraction. When she started doing genealogical research, I helped her put her giant redwood of a family tree together.
At the same time, we were clearing out Grandma's house in the Valley to put it on the market.
In the back of Grandma's Danish modern buffet cabinet, I found a very old, deeply yellowed menu from a Chinese restaurant. I couldn't tell how old it was, but based on the condition and font style, I'm guessing it was at least 60 years old (I've spent my entire life around vintage and antique items and can guess the era correctly most of the time).
Later that day, I pulled up Google Maps and entered the restaurant's address (listed on the front of the menu) to see if it still existed. It was long gone - if the building were still there, it would be on Castelar Elementary School's campus.
I zoomed in for a closer look and spotted something strange. Something that made no sense at all.
"Public Art - 'Jeanne d'Arc'".
I clicked on it.
Joan of Arc was standing smack in the middle of Chinatown, outside of a hospital building.
What the hell?!
So I started Googling. I found out pretty quickly that the Pacific Alliance Medical Center was previously the French Hospital.
What the hell?! Since when did LA have a French Hospital?
Since the cornerstone was laid in 1869, as it turned out. That hospital celebrated its 100th anniversary when my mom was in high school. But she never knew it existed until I told her about it. Mom grew up miles away in Santa Monica/Mar Vista, and my grandparents definitely weren't socially active in what little remained of LA's French community.
Every answer led to more questions. Jean-Louis Vignes, the Sainsevains, the Nadeaus, the Mesmers, the Pellissiers...and more. So many more. And one question loomed over all the rest: why was this sizable, once-thriving community missing from LA's narrative?
Five years later, I keep running lists of people I want to profile on this blog. I keep lists of forgotten French families in greater LA whose lives are, as of now, still a complete mystery to me. I keep lists of places where I need to do serious research when I can get some time off. I've plotted well over 400 sites associated with Southern California's forgotten French on a Google Map (and I'm nowhere near done).
I'm still finding out how deep the rabbit hole goes. And now you know: it began five years ago with a yellowed, crumbling menu from a long-forgotten Chinese restaurant. (In an interesting turn of events, some of this blog's biggest supporters are members of the Chinatown community.)
Friday, January 12, 2018
Something is Rotten in Frenchtown
I strive to do that on this blog (barring the musical interludes).
I *could* petition the city of Los Angeles to turn a weedy vacant lot in the industrial core (formerly the original French Colony) into a French-themed tourist attraction à la Olvera Street...but I am not Christine Sterling and I don't think it's the best possible answer. There are still authentic surviving sites associated with the French in Los Angeles, and at least one of them would make a great museum.
And history museums, unlike tourist attractions, are expected to present the truth.
I've uncovered some uncomfortable truths in the course of my research (and the more research I do, the more I cringe at all of this):
- Seemingly reliable resources can conflict with each other. There are things I haven't blogged about yet because I'm not yet sure which version of a story is correct (and unlike some people, I actually care about getting the facts straight).
- The city of Los Angeles itself is an unreliable source at best. The most glaring example: Damien Marchesseault was elected Mayor SIX TIMES. He was one of LA's most popular mayors of all time. Yet, he does not appear on the city's official list of former mayors, and the memorial plaque in the Plaza that bears his name includes incorrect information (two months ago, the venerable Jean Bruce Poole had me take her to the marker and show her what was wrong with it). He has been erased from LA's narrative so thoroughly that we don't even know what he looked like (no surviving pictures have ever been found). The fact that Marchesseault Street is slated for a return to the map is nothing shy of a miracle. (Part 2 of that story coming soon.) Was Marchesseault erased by political rivals after his death, or was he forgotten so readily because his final term ended under an ugly storm cloud of scandal and suicide? (I'm going to find out. I'm not sure how, but I know I'm going to do it.)
- Wikipedia can bite me. In spite of the fact that it's a nightmare to edit, anyone can edit Wikipedia, and it's just too easy for someone with incorrect information (or worse, an agenda) to misinform anyone gullible enough to take the site's content at face value. Example: The last time I checked, the site claimed that LA's New Chinatown was previously Little Italy. While there were significant numbers of Italian immigrants in the neighborhood, the article fails to note that it was part of Frenchtown first. In fact, that's WHY Italians were attracted to the area. LA's French welcomed Italian immigrants - two founding members of the French Benevolent Society were, in fact, Italian. St. Peter's Church, long linked to LA's Italian community, was originally a cemetery chapel built in honor of French-born André Briswalter (the current building is from the 1940s, and it isn't clear if Briswalter is still buried on the site). And the various French-owned vineyards already clustered in the area would have spelled job opportunities to Italian immigrants with winemaking skills. No one talks about any of this (except me)...yet the vast majority of people reading that entry are going to take it at face value (in spite of the fact that to local historians, it is glaringly incomplete).
- LA's various French organizations (and the French consulate) have never responded to any of my requests for information and/or interviews. At one point, I even asked my dad if his boss would mind sending my contact information to the consulate through a French government employee he knows (the French are formal; we like introductions). Yeah...that didn't work either. (I've had many a question about why I have yet to publish anything on current French entities in LA. Now you know. I'm used to being ignored - but not by people/organizations with whom I have a shared goal. It's indescribably frustrating.)
- I'm ALREADY getting pushback on my idea for a museum. Someone I met recently very pointedly told me (more than once!) that the Pico House hosted an exhibit on the French in LA "a couple of years back". That exhibit ran from late 2007 to early 2008 - TEN years ago. Also, it ran for less than six weeks, wasn't well executed (photos on a wavy plastic wall with no physical exhibits? Are you kidding me? The French are responsible for some of the finest museums in the world...we can do SO much better than that), and has been forgotten by pretty much everyone else. I realize getting a museum open can easily take 10+ years, cost an absolute fortune, and require dealing with a lot of red tape (the Historic Italian Hall Foundation, which was founded to restore the Italian Hall and reopen it as a museum, was founded in the 1980s...and the museum opened in 2016). But, given what we're constantly up against, shouldn't historians and other concerned Angelenos work together to keep the rare surviving scraps of Old Los Angeles alive instead of writing off ideas that don't necessarily fit into a personal agenda?
- I keep finding factual errors in other historians' work. I don't want to diminish the importance of their research and accomplishments. I really don't. However, LA's forgotten French community was filled with amazing people who did amazing things, and I believe we owe it to them to AT LEAST tell their stories correctly.
P.S. In the meantime, I'm speaking at StaRGazing 2018, Greater Los Angeles Area Mensa's annual Regional Gathering. I'm scheduled for 3:20-4:40pm on Saturday, February 17. See you in San Pedro! (Get your ticket NOW. Seriously.)
Monday, November 13, 2017
The Fate of the French Hospital
Putting aside the fate of one of the last surviving relics of LA's obliterated French community (I'm sure I don't need to comment on how I feel about THAT), there is the issue of downtown LA still needing hospital facilities.
When the hospital changed hands in 1989, it came very close to closing entirely, and was saved by a hardworking team of medical professionals, local Chinatown residents, and a generous benefactor in Japan. The 1980s was a rough decade for downtown, and several hospitals in the area (chief amongst them Linda Vista) closed entirely.
To date, I have mapped over 400 French-associated sites in Southern California. The French Hospital - the site where this journey began - was the first place I mapped. The French Hospital survived some of downtown's darkest days...only to be felled 28 years later by the cost of earthquake retrofitting (as I don't have a legal or medical background, I don't feel qualified to comment on the lawsuit mentioned in the linked article).
What will happen to the building? I wish I knew.*
The hospital building has no landmark status or other protection (in spite of being LA's second-oldest surviving hospital**...and in spite of the long-empty Japanese Hospital in Boyle Heights being landmarked).
For once, I don't have any pithy commentary to add. I'm too sad.
*I know it's not the original building from 1869. However...Chinatown legend has it that part of the original adobe hospital building is encased somewhere within the current facility's walls. If the building ends up falling to the wrecking ball and a section of 158-year-old adobe wall turns up, SOMEBODY PLEASE TELL ME. If it still exists (and I realize this is an extreme long shot), it belongs in a museum. (Even if it's badly damaged and looks like hell, if it's survived at all, it's still part of our heritage and still worth saving.)
**The article claims the French Hospital is LA's oldest. It's not - St. Vincent's is older. Also, the hospital was established in 1869, making it 158 years old, not 157 as the article claims.
Saturday, June 3, 2017
Deed Restrictions and the Renaming of Frenchtown
The first, and most revealing, question in the Q&A concerned why LA's historically French neighborhoods are now associated with other ethnic groups.
The original Frenchtown - bordered by Main Street, 1st Street, Aliso Street, and the LA River - is now largely split between Little Tokyo and the industrial core, with the Civic Center bleeding into the northern end of the neighborhood.
As Frenchtown expanded to the north, it grew to include modern-day Chinatown. Why is Joan of Arc standing outside Chinatown's only hospital? Because it was the French Hospital until 1989, and until the 1930s, it was a French neighborhood. Naud Junction, the Fritz houses, and Philippe the Original (creators of the French Dip sandwich; in that location since 1951) are all in Chinatown for the very simple reason that it wasn't always Chinatown. (LA's original Chinatown was demolished in 1931 to build Union Station - long after the Sainsevain brothers lost their uncle's vineyard).
Pellissier Square is now called Koreatown. Why? Because much of central LA declined after the 1930s, making it an affordable place for Korean immigrants to live and start businesses by the time the Korean War ended.
They weren't the first Koreans in Los Angeles. Historically, Korean Angelenos tended to live in Bunker Hill.
(Incidentally, "Koreatown" is something of a misnomer. HALF of Koreatown residents are Latino, and only about one-third are Asian. Korean Angelenos do, however, account for most of the area's businesses.)
There are still clues to Koreatown's French origins. Normandie Avenue, one of the longest streets in Los Angeles County (stretching 22.5 miles between Hollywood and Harbor City), runs smack down the middle of Koreatown. The Pellissier Building, including the legendary Wiltern Theatre, proudly towers over Wilshire and Western. And if you look at the neighborhood's architecture - sure, it's largely Art Deco, but some of it is also French-influenced.
In the early days, Los Angeles was a fairly tolerant place. It wasn't a utopia by any means (case in point: the Chinese Massacre of 1871), but Los Angeles was more tolerant of non-WASPs than most North American cities.
By the 1920s, a plague began to infest Los Angeles on a grand scale.
Deed restrictions.
Sometimes called restrictive covenants, deed restrictions barred ethnic and/or religious groups from buying homes in particular areas.
Why? Who would do something so hateful?
Let's start by rewinding the clock to the 1850s.
In 1850, California became a state. Legally, Los Angeles should have started opening public schools at this point (due to separation of church and state), but LAUSD wasn't founded until 1853. By this time, there was a growing number of Protestant families - most of them Yankees - in town. The few schools that did exist in the area were all Catholic, and Protestant parents objected - loudly - to the idea of sending their kids to Catholic schools. (Many Catholic schools do accept non-Catholic students, and many non-Catholic parents may prefer them if the local public schools aren't good enough. But things were a little different 164 years ago.)
Fast-forward to the 1880s.
When railroads first connected Southern California to the rest of the United States, newcomers flooded the area. Most were WASPs, and the majority were from the Midwest.
Guess where else deed restrictions were common? That's right - the WASPy Midwest. (No offense to any WASPs or Midwesterners who may read this, but I don't believe in hiding the truth. I sure as hell have never pretended French Californians were perfect.)
Before too long, deed restrictions barred people of color from much of the city. Some even excluded Jews, Russians, and Italians. Homeowners' associations and realtors often worked together to keep restricted neighborhoods homogeneous. (My skin is crawling as I write this.)
Excluded ethnic and religious groups, therefore, tended to live in areas that weren't restricted against them.
French Angelenos, however, were a pretty tolerant bunch.
The first baker in the city to make matzo was Louis Mesmer, who was Catholic. His daughter Tina married a Protestant.
Harris Newmark - German and Jewish - was one of Remi Nadeau's best friends.
Prudent Beaudry's sometime business partner Solomon Lazard - French and Jewish - was so popular among Angelenos of all ethnicities that Spanish speakers called him "Don Solomon".
French Basque Philippe Garnier built a commercial building specifically to lease it to Chinese merchants, who weren't considered human beings by the United States government at the time.
No one batted an eye at the fact that quite a few of LA's earlier Frenchmen (including Louis Bauchet, Joseph Mascarel, and Miguel Leonis) married Spanish, Mexican, or Native American women.
Frenchtown didn't have deed restrictions. (It's true that we don't always get along with everyone, but you won't find many French people willing to do something that asinine.)
The original core of Frenchtown was largely taken over by the civic center and industry when the area was redeveloped in the 1920s (and when the 101 sliced through downtown). But part of it became Little Tokyo. Why? No deed restrictions.
In fact, when Japanese American internment emptied Little Tokyo during World War II, African Americans (many working in the defense industry) poured into the neighborhood, and for a time it was known as "Bronzeville". Again, it was still one of the few areas with no deed restrictions. (On a personal note, the original paperwork for my childhood home in Sherman Oaks - built in 1948 - included a restriction against selling to African Americans. No other ethnicities were excluded. Which should give my dear readers a rough idea of what African American home buyers faced at the time - and renters had even fewer choices. Deed restrictions were legally struck down in California in 1947 and nationwide in 1948, but in Los Angeles, they persisted into the 1950s. Nationwide, it was probably worse.)
LA's original Chinatown was emptied and razed to build Union Station. Where did all the Chinese Angelenos go? The area now known as Chinatown was full of French Angelenos first. Wikipedia incorrectly states that it was originally Little Italy. It's true that Italians did live in the neighborhood, but the French arrived before the first Italians did, and made up a larger percentage of the population. Why did the demographics change? No deed restrictions to keep out Chinese residents - or, for that matter, Italian residents. (Catholics of all origins occasionally clashed with Chinese Angelenos over religious differences, but the French community welcomed newcomers from Italy. Case in point: two of the French Benevolent Society's founding members were Italian. And the French Hospital did accept Chinese patients at a time when most hospitals wouldn't.)
LA's Jewish community was largely based in Boyle Heights for many years. Guess who else lived in Boyle Heights back in the day? There were Anglos, sure, but there were also Basque farmers. In fact, Simon Gless' big Victorian house was used as office space for the Hebrew Shelter Home and Asylum for many years (the last time I checked, it was a boarding house for mariachi musicians). Once again - no deed restrictions. (Why does Los Angeles County have so many Jewish residents? Because Jews have, historically, been more welcome in Los Angeles than in many other places. Los Angeles was a tiny frontier town when the first Jewish residents arrived, and in the Old West - where people had to work together to stay alive - how you treated people mattered more than what house of worship you attended.)
I haven't found anything on whether Pellissier Square ever had deed restrictions or not, but there's a reason Korean Angelenos originally clustered in Bunker Hill. Prudent Beaudry - who developed for everyone - developed Bunker Hill. Like Angelino Heights, Bunker Hill was unrestricted.
How did Frenchtown cease to be called Frenchtown?
Simple. As the city expanded westward, and as many French Angelenos moved west or left the city entirely in search of land for grazing livestock/farming/growing grapes, people who weren't welcome in other areas moved to the historically French - and historically unrestricted - neighborhoods.
If you were in the same situation, wouldn't you?
Friday, April 28, 2017
We're Still Here, Part 2: Chinatown
Not too far from Bauchet Street, Mesnager Street intersects with Naud Street.
Joan of Arc, erected in 1964, still stands proudly outside the old French Hospital.
The French Hospital, founded in 1869 by the French Benevolent Society, still exists. The original adobe building and wood-framed nurses' dormitory were replaced long ago. (A portion of the original hospital is rumored to be entombed somewhere inside the hospital's walls.)
Poor Joan almost seems lost outside the modern-day Pacific Alliance Medical Center, as the French Hospital has been known since 1989.
Angels Walk information stanchion outside the hospital. Note the references to LA's French mayors, the water system, Le Progrés, and French being more commonly spoken than English.
What's this? Another Angels Walk stanchion?
Note references to the Fritz houses. Philippe Fritz, a carpenter from Alsace-Lorraine, built three houses next to each other for his family. One house was later moved to Wilshire and Normandie (and is, of course, no longer there, either).
Same stanchion, outside the Chinatown Heritage and Visitors Center. Look, it's Mayor Beaudry!
More on the water system. Until well into the twentieth century, French Angelenos were instrumental in bringing water to Los Angeles residents.
One of the Fritz houses.
Another angle on the same house.
A wider angle on the first house. Now this is the home of a carpenter.
And where are the Fritz houses? Bernard Street! Jean Bernard held a grant deed for this part of town, and ran a brickyard nearby.
Edited to add (7/1/17): If you've seen La La Land, you've seen Bernard Street - sort of. In the scene with Mia leaving a voicemail for Sebastian, she does walk down Bernard Street (you can see the street sign and the Chinese-themed motel on the corner). Mia is walking opposite the Fritz houses. It's such a wasted opportunity to show another aspect of LA's culture and charm, but sadly, French Angelenos receive little to no representation anywhere (let alone in an Oscar-winning film).




















