Tales from Los Angeles’ lost French quarter and Southern California’s forgotten French community.
Friday, March 22, 2019
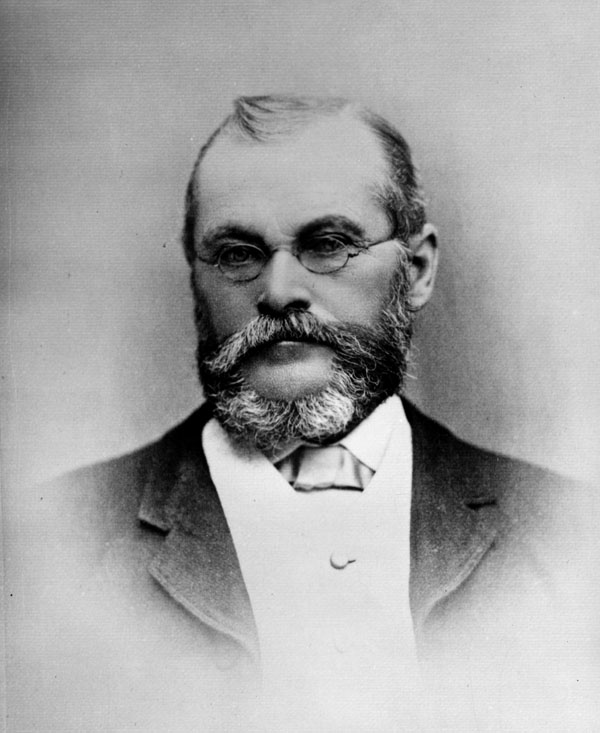
Eugene Meyer: A Nameplate, a Cemetery Plot, and Old LA's Best Department Store
Meyer's haberdashery, the first in Los Angeles, stood at 4th and Main, near Raymond Alexandre's Roundhouse. Coincidentally, when the Roundhouse hosted a 3,000-person Centennial celebration in 1876, Eugene Meyer was one of the parade's four marshals.
Meyer, like several other French Angelenos, belonged to the International Order of Odd Fellows' Golden Rule Lodge. In 1867, he married Harriet Newmark. They had eight children.
Harris Newmark (Meyer's cousin-in-law) reported that while he was away in New York for an extended period, Eugene and Harriet Meyer added a silver nameplate to their front door. This was such a rare sight in 1860s Los Angeles that Newmark's family mentioned it to him in a letter - and when Newmark inspected it himself a year later, the nameplate was still a novelty.
In 1872, while Meyer was serving as President of the French Benevolent Society, he asked the Los Angeles City Council to allocate a plot in the City Cemetery for Society members. The City Cemetery became (drumroll please...) a parking lot many years ago, but for as long as it lasted, it did have a plot for the French Benevolent Society. (Most notably, Mayor Damien Marchesseault, ineligible for burial at Calvary Cemetery due to his suicide, was buried in the French Benevolent Society's plot. He was later re-interred at Angelus Rosedale.)
Meyer was a founding member of the Los Angeles Board of Trade (now the Chamber of Commerce) when it was established in 1873. The following year, he was one of several prominent French Angelenos who tried to persuade railroad officials to locate their depot east of Alameda Street, between Commercial and First Streets. This proposed location was close to the city's economic center, and many French Angelenos conducted business in the area. However, the railroad demanded control over the west side of Alameda Street as well, which was out of the question to area business owners.
In 1874, Solomon Lazard sold the City of Paris department store to Eugene and his brother Constant Meyer, who expanded the business. City of Paris carried sporting goods, housewares, shoes, toiletries, cameras, luggage, umbrellas - and clothing. In fact, all the elegant ladies of Old Los Angeles bought the latest in French fashions from City of Paris. The store also had an in-house travel agency, chiropodist's office, shoeshine parlor, beauty parlor, and library...and Los Angeles' French consulate! In addition to his job as co-owner of the city's premier department store, Eugene Meyer served his home country and his adopted city as a consular agent.
By 1883, the store was listed in directories as both City of Paris and Eugene Meyer & Co.
The Meyers moved to San Francisco in 1883 so Eugene could manage Lazard Fréres' new California branch (which would close in 1906 due to the San Francisco earthquake).
Eugene's son Eugene Meyer Jr. went on to work at Lazard Fréres himself before striking out on his own as a speculator, investor, and eventual co-founder of Allied Chemical & Dye, which eventually became part of Honeywell's specialty-materials branch (there is a building named for Eugene Jr. at Honeywell's headquarters in New Jersey). He eventually became Chairman of the Federal Reserve and purchased the Washington Post in 1933.
Eugene Jr.'s daughter Katharine Meyer Graham, who succeeded him as the newspaper's publisher, needs no introduction.
Friday, April 26, 2019
Leon Loeb and the City of Paris
Loeb married Harris Newmark's oldest daughter, Estelle, in 1879. They had four children - Edwin, Joseph, Rose, and George (sadly, George only lived a few months). He was active in local French circles, active in charitable circles, active in Congregation B'nai B'rith, and is said to have held every office in Odd Fellows Lodge No. 35.
When Eugene Meyer stepped down to move to San Francisco, Leon Loeb took over as head of the firm and took on new partners. The company name was changed to Stern, Loeb, & Co., but after a while, Loeb had a better idea.
Loeb decided to rebrand the dry goods store as a classy department store. And a classy department store needs a classy name.
Loeb was French. Solomon Lazard was French. Eugene Meyer was French. All the best stuff (at least in fashion) was imported from France - especially Paris.
By now, you know Solomon Lazard's dry goods store eventually became the Ville de Paris. And now you know who deserves the credit for that clever idea - Leon Loeb.
Loeb also took over Eugene Meyer's duties as a French consular agent. After fifteen years of service (working his way up to vice consul), the French government gave him two high honors - Chevalier du Merit Agricole and Officer d'Academie.
For the past 11 days, the world, including Los Angeles, has mourned the devastating fire at Notre Dame de Paris. This isn't the first time Los Angeles has mourned a tragic fire in Paris.
Paris' French Catholic upper class held an annual charity fundraiser, the Bazar de la Charité. In 1897, a combination of a wooden event building, lots of flammable materials, improperly marked exits, and a malfunctioning cinematograph caused a fire that killed 126 people.
A requiem mass was held in Los Angeles "at the old mission church" (the article doesn't specify whether it was Mission San Fernando, Mission San Gabriel, or the technically-not-a-mission Plaza Church). Leon Loeb attended the mass in his official capacity as a representative of the French people.
Newspaper accounts indicate that Leon Loeb served on the Bastille Day celebration committee several times, usually as honorary president or vice president.
When Rabbi Abraham Wolf Edelman passed away in 1907, Leon Loeb was one of the honorary pallbearers.
Loeb later went to work with his father-in-law as treasurer (and part owner) of H. Newmark & Co. By 1910, the census listed Loeb as living in Newmark's house on West Lake Avenue.
Leon Loeb passed away in 1911 at the age of 66. He is buried at Home of Peace Memorial Park in East Los Angeles.
Leon's surviving sons, Joseph and Edwin, both became attorneys. After working at other firms, they founded the law firm of Loeb & Loeb, with Joseph handling their corporate clients and Edwin handling movie studio clients. More than a century later, Loeb & Loeb has offices in several U.S. cities and in China.
Sunday, April 14, 2019
Edgar J. Meyer Died on the Titanic
In any case, he was still the son of a prominent French Angeleno - Eugene Meyer. I already profiled his father, mentioning his brother Eugene Jr. and his niece Katherine, so to heck with it. Los Angeles tends not to have many connections to notorious events like this one.
Edgar J. Meyer studied mechanical engineering at Cornell University, where he discovered a method of measuring velocity of flame propagation in gas engines (I have no idea what that means, but this method was reportedly added to textbooks). Regardless, Edgar chose to join older brother Eugene Jr. in business on Wall Street. In 1909, he married Leila Saks, who was born in Baltimore to German parents. Their only child, Jane, was born in 1911.
The Meyers were never supposed to be on the Titanic. They had been traveling in Europe when they received the news of Leila's father's death, and quickly arranged passage home.
Edgar and Leila boarded the ship on April 10 in Cherbourg, holding first-class tickets. Late at night, four days later, disaster struck.
Leila Saks Meyer recalled:
I tried and tried to get Edgar to come into the lifeboat with me, and pleaded to be allowed to stay behind and wait until he could leave, he not caring to leave before all the women had been saved. Mr. Meyer finally persuaded me to leave, reminding me of our one-year-old child at home. I entered the lifeboat and watched until the Titanic sank, but only for a short time did I see my husband standing beside the rail and assisting other women into boats in which he might have been saved.One year later, Harris Newmark wrote:
In common with the rest of the civilized world, Los Angeles, on April 15th, was electrified with the news of the collision between an iceberg and the great ocean steamer Titanic which so speedily foundered with her 1535 helpless souls. For a day or two, it was hoped that no one with Los Angeles connections would be numbered among the lost; but fate had decreed that my nephew, Edgar J. Meyer, a son of Mr. and Mrs. Eugene Meyer, should perish. He was one of those who heroically hastened to the aid of the women and children; nor did he rest until he saw his wife and child placed in one of the lifeboats. They were saved, but he went down...(Newmark must not have realized the Meyers hadn't brought their baby daughter on the trip.)
Edgar J. Meyer's body was either never recovered or never identified. He was 28 years old.
Wednesday, March 1, 2017
Raymond Alexandre and the Roundhouse
Raymond Alexandre was a sailor, born in France but well-traveled. (His rank and exact birthplace seem to be lost to history.) Alexandre was an early French arrival, landing in town before 1850, and kept a saloon near Requena Street (where Harris Newmark spent at least one smoky evening with his trigger-happy friend Felipe Rheim).
In 1854, Alexandre built a two-story, cylindrical house with a hut-style roof at the corner of 3rd and Main Streets (which was, at the time, some distance from the pueblo). The house was allegedly inspired by a stone building he had once sighted on the African coast, and Alexandre built it for his new bride, Maria Valdez. (Alexandre used adobe instead of stone, as adobe was far more readily available at the time.)
Madame Alexandre wasn't impressed by her husband's architectural flight of fancy. (Given that this highly unusual house, inspired by an exotic location, was built roughly 80 years before storybook style came to Los Angeles, I feel comfortable calling it Southern California's earliest known example of fantasy architecture.)
Alexandre sold the Roundhouse to German-born George Lehman. In 1856, Lehman converted the house and its grounds into LA's first amusement park, The Garden of Paradise.
The Garden of Paradise was essentially a family-friendly beer garden that boasted a plethora of exotic plants, live music, and games for children. For over twenty years, it was a very popular Sunday destination. Lehman eventually added the wood paneling that gave the house its later octagonal look. Harris Newmark recalled that prickly pear cacti bordered the Roundhouse's gardens, and visitors freely picked the bright pink fruit.
On July 4, 1876, the Roundhouse hosted a centennial celebration for 3,000 people. Southern California's first large-scale parade began at the wool mills on Aliso Street and ended at the Roundhouse's grand party, featuring a French Benevolent Society chariot. One of the celebration's four marshals was Eugene Meyer, an accomplished Frenchman we'll meet again later.
Unfortunately for George Lehman, he accumulated debts he couldn't pay and lost the Roundhouse to foreclosure. The building was re-purposed as a schoolhouse, and Southern California's first kindergarten classes were taught there. Incidentally, Kate Douglas Wiggin (author of Rebecca of Sunnybrook Farm) trained as a kindergarten teacher at the former Roundhouse.
Raymond Alexandre's unique African/Spanish house was torn down in 1889. Today, the site is largely occupied by government buildings.
Thursday, July 14, 2022
Bastille Day in Old LA
On this day in 1789, the French Revolution began.
I an pretty open about having a complicated relationship with La Fête Nationale/Bastille Day. My dad is a descendant of an earlier French monarch, which makes both Louis XVI and Marie Antoinette my very distant cousins. My mom's family comes from centuries of French peasant stock.
Still, I wish I could take a time machine to Old LA on this day. The French community put on quite a Bastille Day celebration.
In fact, it used to be a pretty big deal in LA.
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1881 |
One of the earliest references I can find lists the parade route: Aliso to Arcadia, Main to the Plaza, then to Spring, Spring to Second, Second to Fort (Broadway), Fort to Fourth, Fourth to Main, Main to the junction with Spring, and to the Turnverein Hall for speeches. "A representation of the Bastille" (i.e. a very early parade float) was included in the procession.
This route would have effectively started in the French Colony, gone to the Plaza, doubled back and wound through downtown, ending up where the Convention Center parking lot is today. For comparison, the Rose Parade follows a roughly 5.5 mile route.
Two of the speakers were Pascal Ganée and Georges Le Mesnager, who was quite well known for his speeches! More on that in a minute.
Bastille Day 1881 concluded with a banquet at the Pico House, prepared under one of LA's early celebrity chefs, Victor Dol.
On this day in 1882, the festivities began with a 21-gun salute at sunrise from Fort Hill. The Mayor, the President of the City Council, "delegates from fire companies and civil societies", French citizens of varying prominence, and a beauty queen - the Goddess of Liberty - all made appearances.
The Goddess of Liberty chosen for the event, by the way, happened to be 14-year-old Narcisse Sentous, eldest daughter of Jean Sentous. She was carried in a "Car of Liberty" with several maids of honor, all girls from the French Colony.
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1882 (snippet of much longer article) |
The parade procession was big enough to have two divisions, both made up of prominent citizens and local societies. Besides the Car of Liberty, another car had Marie Deleval representing France, Mathilde Reynaud representing the United States, Honoré Penelon (eight-year-old son of the late Henri Penelon) dressed as the Marquis de Lafayette, and ten-year-old Auguste Lemasne dressed as George Washington. Rounding up the rear were citizens riding donkeys in tribute to the city's butchers.
Eugene Meyer, the "President of the Day" (i.e. Grand Marshal) and then-Agent for the French consulate, gave a speech in French and introduced Frank Howard (who gave a quick history lesson on Bastille Day in English). "The Star-Spangled Banner" was sung, the band played, "La Marseillaise" was sung, and Georges Le Mesnager gave a speech in French.
And that wasn't all. A large model of the Bastille had been built on Fort Hill. After the sun went down, it was stormed and set on fire. (Good thing two fire companies were there!)
The day concluded with a party at Armory Hall.
In 1886, the French Colony invited the editor of the Los Angeles Herald to attend the Bastille Day celebration. He had a prior commitment in Long Beach that day, but thanked the French Colony in the newspaper.
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1886 The newspaper did still cover the event, of course. In spite of a half-hour rainstorm (an extreme rarity during a Southern California summer), the parade went on, although many people who had planned to join the parade waited inside the French Theatre for the rest of the day's events. The President of the Day was Jean-Louis Sainsevain this time - and again, one of the last speeches was given by Georges Le Mesnager. The biggest celebration of them all was held in 1889 - the 100th anniversary of the French Republic. Besides the usual festivities, an extravagant banquet and ball was held at the Pico House, then owned by Pascal Ballade and renamed the National Hotel. The speech Georges Le Mesnager gave on this day was particularly well remembered by French Angelenos - and you can read most of it (thoughtfully translated into English by the Los Angeles Herald) here. |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1891. |
An interesting footnote to the 1891 celebration is that one of the vocalists was J.P. Goytino, who despite having some musical talent was also a highly problematic newspaper editor/slumlord/all-around dirtbag. Goytino is perhaps most notorious for stopping issuance of a marriage license five years later when his extremely wealthy father-in-law, Joseph Mascarel, sought to legally marry his common-law second wife. (He needn't have bothered; Mascarel left most of his fortune to his grandchildren from his first marriage.) I could do a pretty ugly deep dive on Goytino, but David Kimbrough already did a very thorough one on Facebook (warning: it's a 12-parter).
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1900 |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1901 |
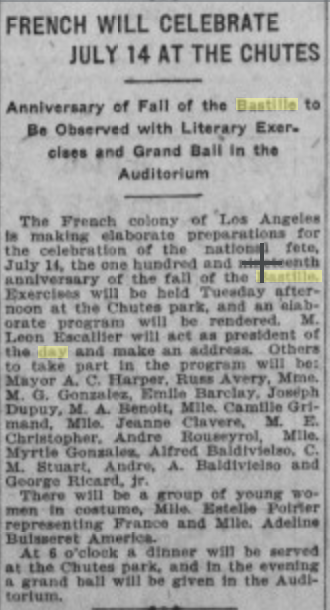 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1908 |
 |
| Los Angeles Herald, 1908 |
 |
| Hollywood Citizen-News, 1940 |
 |
| Los Angeles Times, 1947 |
After the war, Bastille Day was back - and hosted by the Los Angeles Breakfast Club!
 |
| Los Angeles Daily News, 1949 |
Los Angeles Times, 1951  |
| Los Angeles Times, 1957 |
 |
| Highland Park News-Herald and Journal, 1957 |
 |
| Los Angeles Times, 1960 |
Bastille Day was a big enough event to merit an annual flag ceremony at City Hall and draw a crowd of thousands to the Colony’s celebration. That certainly isn't the case now, and I fully expect Mayor Garcetti to ignore Bastille Day again, as Mayors of Los Angeles have tended to do for years.
Wednesday, June 14, 2017
We're Still Here, Part 3: The San Fernando Valley
Because it IS my home. I'm a genuine, authentic Valley girl (hang around me long enough and you just might detect bits of my old accent).
(Well, it was my childhood home, anyway. I've lived in various beach towns continuously since 2001.)
Let's start in Calabasas and work our way east...
Michel Leonis, nicknamed "Don Miguel" out of fear rather than respect, discovered a dilapidated adobe house on the grounds of Rancho El Escorpion (huge naming opportunity missed here: Rancho El Escorpion sounds so much more badass than Calabasas - Spanish for "squashes"). He and his Chumash wife, Espiritu Chijulla, fixed it up (enclosing the rear staircase and adding the balcony), moved in, and lived here until their respective deaths.
The house - long empty and once again severely neglected - was nearly torn down in 1962 for - you guessed it - a supermarket parking lot. Thankfully, it's still with us today.
(I will devote separate entries to Leonis and to the Leonis Adobe Museum.)
Moving east, we find...
Running north-south from Ventura Boulevard to Granada Hills (okay, fine, it's interrupted in a couple of places), Amestoy Avenue was named for another French Basque ranching family - the Amestoys.
(The Amestoys will get their own entry.)
Just a few blocks east of Amestoy Avenue is one of their former homes - Rancho Los Encinos.
Four French and French Basque families - Garnier, Oxarat, Gless, and Amestoy - owned the rancho in turn. The original adobe is on the right. The two-story house on the left was built by the four Garnier brothers to house the rancho's employees, and is said to be a copy of the family home in France.
Although slightly beyond the scope of this entry, but worth noting, is the fact that Eugene Garnier once testified against Michel Leonis in court. Leonis, a brutal and terrifying thug who added to his vast land holdings through harassment and intimidation, burned the Garniers' newly planted wheat field and beat their employees. Eugene stated in court that he was testifying only because he was forced to do so, and later returned to France. His brother Philippe Garnier, bloody but unbowed, went on to build the Garnier Building and lease it to Chinese tenants.
I include this photo as proof that culture and beauty do, in fact, exist in the Valley if you know where to look. The Garnier brothers were legendary for their hospitality - so much so that Pio Pico's brother Andrés used to bring very special guests all the way to Rancho Los Encinos (from what is now downtown) - ON HORSEBACK. For BREAKFAST.
And those very special guests dined in the Garniers' grand salon, which boasted the most striking faux marbre walls in the history of Los Angeles. (I hope someone else takes the time to notice that the plastic food on the table is French in theme - grapes, brie, asparagus, and crusty-looking bread.)
At some point, an incredibly foolish individual elected to plaster over the faux marbre. The adobe was severely damaged in the Northridge earthquake of 1994, but with one silver lining - much of the plaster covering the salon's elaborately painted walls fell off. (Portions of the offending plaster remain. This is a very delicate old house, and that paint is well over 100 years old. Some things are best left well enough alone.)
(All four families merit, and will get, their own entries. Ditto Los Encinos State Historic Park, where the adobe and the ranch hands' quarters are located.)
The Amestoy family - the last French owners of the rancho - held onto much of the land (including these buildings) until 1944. After World War II, Rancho Los Encinos was subdivided into (what else) Encino and (my neck of the woods) Sherman Oaks.
On a personal note, my mother was completely shocked to learn that the Los Encinos adobe was a) still standing, b), continuously French-owned for much of its existence, c) right above Ventura Boulevard (a thoroughfare my family knows pretty well), and d) less than six miles from our old house in Sherman Oaks. She's said that if she had ANY idea, she would have taken me there when I was a child (in addition to Olvera Street, Chinatown, etc.).
Moving further east...
A street in Mission Hills was named for onetime mayor Joseph Mascarel. I suspect he owned land in the area (he owned significant amounts of land in FOUR counties). Today, he is so little-known that whoever made this sign didn't bother to check the spelling.
Heading further east...
Solomon Lazard was both French and Jewish, and was so popular with Angelenos of all ethnicities that he was nicknamed "Don Solomon" and often acted as floor manager for fandangos. He was the first President of the Los Angeles Chamber of Commerce, co-founded the City Water Company (later LADWP) with Prudent Beaudry and Dr. Griffin, founded the City of Paris department store (which he later sold to his cousins, Eugene and Constant Meyer), and was active in the Golden Rule Lodge and the Hebrew Benevolent Society. Today, he's been reduced to a street sign on a cul-de-sac in San Fernando. (There was a different Lazard Street long ago, and Mayor Mascarel lived there until his death. It was renamed Ducommun Street. I'll explain why when I get to Charles Ducommun.)
Heading even further east, we reach our final stop in the furthest reaches of Glendale...
You know who Georges Le Mesnager was. This stone barn was built for his vineyard, located in what is now Deukmejian Wilderness Park. When it was damaged in a fire, his son converted it into a farmhouse - which the family lived in until the 1960s.
The barn has been undergoing a remodel/conversion into an interpretive center.
I knew nothing about any of these places until I began to research LA's forgotten French history - and one of them was just a few miles from my house. Small wonder that most Angelenos have NO idea about Frenchtown.
Tuesday, December 27, 2016
He Built This City: Mayor Prudent Beaudry
Possessing boundless energy, exceptional business sagacity and foresight, Prudent Beaudry amassed five fortunes and lost four in his ventures, which were gigantic for that time, and would be considered immense today.
Have a seat, everyone...the lifetime I'm chronicling this week is best described as "epic".
Jean-Prudent Beaudry was born July 24, 1816 in Mascouche, Quebec - close to Montreal. When he was a young boy, the family moved to the neighboring town of Saint-Anne-des-Plaines.
There were five Beaudry brothers (and three Beaudry sisters). All of the Beaudry brothers worked hard and got rich, but Prudent, Jean-Louis, and Victor would make the history books. (Victor, the only other Beaudry to settle in Los Angeles, will be covered in another entry, because this one is going to be LONG.)
The Beaudrys, an industrious family of traders, sent their sons to good schools in Montreal and New York. Prudent and his brothers had the benefits of a great education and English fluency when they went into business for themselves.
Which they did, many times over.
Prudent started out in his father's mercantile business, then went to work at a different mercantile house in New Orleans, returning to Canada in 1842 to partner with one of his brothers. By 1844, he left the business to join Victor, the youngest Beaudry brother, in San Francisco. The Gold Rush was a few years away, but Victor had already established a profitable shipping and commission business in the city. Before long, the brothers were in the ice business (Victor later partnered with another future mayor, Damien Marchesseault, in distributing ice harvested in the San Bernardino Mountains). Perhaps not surprisingly for a native of Quebec, Prudent also got into the syrup business. Two years later, after Prudent had lost most of his money on real estate speculation (and more of it when insufficiently insured stock was destroyed in a fire), Los Angeles beckoned.
I'll let Le Guide Francais take it from here:
Starting with $1,100 in goods and $200 cash in a small store on Main Street, where the City Hall now stands, it is said that he cleared $2,000 in thirty days, which enabled him to take a larger store on Commercial Street. From that time on, Prudent Beaudry was one of the preeminent men of the economic, social, and political life of the Southwest.(The book, just to clarify, refers to the current City Hall, not the old Bell Block down the street. After Beaudry vacated the Commercial Street shop, Harris Newmark moved in. Ironically, Beaudry sold his dry goods business to Newmark twelve years later.)
Having earned a well-deserved vacation, Prudent left Los Angeles for Paris in 1855. The chief items on his itinerary were seeing the Exposition Universelle and consulting the great French oculist Dr. Jules Sichel. Prudent visited Montreal on his return trip to visit his brother Jean-Louis, who would serve as Mayor of Montreal for a total of ten years between 1862 and 1885. The Beaudrys, needless to say, were just as prominent in business, politics, and society in Quebec as they were in Southern California.
While Prudent was away, Victor was capably managing his brother's business interests. Prudent had purchased a building on the northeast corner of Aliso and Los Angeles Streets in 1854 for $11,000. Victor spent $25,000 - an absolute fortune at the time - on remodeling and improving the building. In this case, it was money well spent. After the Beaudry Block was improved, it was considered the finest building in Southern California for the time. Rents increased from $300 per month to $1,000 per month.
Prudent returned to Los Angeles in 1861 (Victor had been offered a contract to supply the Army of the Potomac and found it difficult to manage his brother's business interests at the same time). He continued in the mercantile business until 1865. Due to stress, he retired...but not for long. The Beaudrys just weren't capable of being unproductive.
In 1867, Prudent Beaudry made one of his greatest real estate investments. The steep hill above New High Street, which he purchased at a Sheriff's Department auction for the pittance of $55 (I can't believe it either), was known as Bunker Hill. It would soon become famous for its Victorian mansions.
This purchase set Beaudry on a path that made him California's first realtor and first large-scale developer, in addition to an urban planner. Before long, he was buying extensive tracts of land, dividing them into lots, and selling them, working out of an office opposite the Pico House. One 20-acre tract, between Charity (Grand) and Hill from Second to Fourth, cost $517 and netted $30,000. Another tract, consisting of 39 acres bordered by Fourth, Sixth, Pearl (Figueroa) and Charity (Grand), earned $50,000.
The Beaudry brothers (smartly) kept buying land. They predicted - correctly, and beyond their wildest dreams - that after railroad lines connected Los Angeles to San Francisco and the East Coast, new settlers would pour into Southern California in droves. (If they could only see how right they were!) Prudent also bought land in modern-day Arcadia and near the Sierra Nevada mountains (building aqueducts to redirect mountain streams to his properties), and helped to found the cities of Pasadena and Alhambra.
One newspaper advertisement from 1873 lists 83 (yes, 83!) separate lots for houses, in addition to two full city blocks, multiple city tracts, and large land parcels in Rancho San Pedro, Verdugo Ranch, and the Warner and de la Hortilla land grants. A similar ad from 1874 notes, in bold, which of the streets with lots for sale had already had water pipes installed. It's no wonder Beaudry was able to keep his real estate business going every time he lost most (or all) of his money.
Severe flooding in January 1868 had undone nearly all of Jean-Louis Sainsevain and Damien Marchesseault's hard work on the city's primitive water system. As a developer, Beaudry was very concerned about improving the city for its residents. On July 22, 1868, a 30-year contract for the water system was granted to the newly-established Los Angeles City Water Company. The three partners in the Company were Dr. John Griffin, French-born businessman Solomon Lazard, and, of course, Prudent Beaudry (most of the employees were also of French extraction - chief amongst them, Charles Lepaon, Charles Ducommun, and Eugene Meyer - more on them in the future).
The Los Angeles City Water Company replaced Sainsevain and Marchesseault's leaky wood pipes with 12 miles of iron pipes, and continued to regularly make improvements on the water system until the contract expired 30 years later (the city purchased the system for $2 million - in 1898 dollars!). Although nothing could cancel out the previous water problems or Marchesseault's tragic suicide, the city of Los Angeles finally had a reliable water system that wouldn't turn streets into sinkholes. (If you live in Los Angeles and you like having running water, thank a Frenchman. Seriously, you guys owe us.)
You're probably wondering how Prudent managed to supply water to his hilltop property. In those days, hills weren't desirable places to build homes because water had to be transported in barrels via trolley or other vehicle. The city water company wasn't interested in solving the problem. But in case you haven't noticed yet, Prudent was smart, resourceful, and didn't give up easily. He knew that if running water was available, prospective homeowners would be more likely to consider hilltop lots and pay a good price for them. So he constructed a huge reservoir and a pump system that supplied water from LA's marshy lowlands to Bunker Hill. The pump system worked perfectly - and so did his plan. (I'll bet every land speculator in Southern California wished they had thought of that.)
Before long, Bunker Hill became THE place to build grand homes. At least two of its fabled Victorian mansions were built for other French Angelenos - entrepreneur Pierre Larronde and model citizen Judge Julius Brousseau.
Let it be known, however, that Beaudry developed for everyone. It's true that he built mansions and had a keen interest in architecture, but he also built modest homes on small lots for working families. And because he made modest properties available for small monthly payments, he made home ownership possible for buyers with lower incomes. He made considerable improvements to his land - paving roads, planting trees, and providing for water usage.
And Beaudry just kept developing land for the rest of his life. This Lost LA article includes an 1868 map showing five tracts recently developed by Beaudry.
The Bellevue tract included a garden he dubbed "Bellevue Terrace". This early park rose 70 feet above downtown, boasting hundreds of eucalyptus and citrus trees. Beaudry eventually put the site up for sale. The State of California bought it to develop a Los Angeles campus of the State Normal School, which would later become UCLA. When UCLA moved to Westwood in the 1920s, the hill was graded down and replaced with Central Library.
A few miles away, where North Beaudry Avenue meets Sunset Boulevard, there is an oval-shaped parcel of land that currently holds a church, a restaurant, and The Elysian apartment building. In the early 1870s, this was Beaudry Park - another garden paradise on a hill, boasting citrus groves and eucalyptus trees (and vineyards!). But the Beaudrys put it on the market a decade later. The Sisters of Charity snapped it up in 1883, building a newer facility and relocating St. Vincent's Hospital (sometimes called the Los Angeles Infirmary) here.
Beaudry owned a large tract containing one block of stagnant, foul-smelling marshland. No one wanted to build on the land, and it wasn't ideally suited to building anyway. In 1870, Beaudry got the idea to drain the marsh and turn the land into a public park. Naturally, he spearheaded the plan. Originally called Los Angeles Park, the land was renamed Central Park in the 1890s...and was renamed again later.
You know this park. There's a good chance you've been there (and there's a VERY good chance you absolutely hate its current incarnation).
Give up yet?
It's Pershing Square. (It used to be a very nice park. Trust me on this.)
Beaudry's dedication to developing, planning, and improving the city got him started in politics. He was elected to the Los Angeles Common (City) Council for three one-year terms (1871, 1872, and 1873). In 1873, he became the first president of the city's new Board of Trade. His name appeared in Los Angeles newspapers frequently throughout the 1870s and 1880s - mostly in the real estate sections (and in a bankruptcy case...the Temple and Workman Bank failed and took most of his money with it).
In 1874, Prudent Beaudry became Los Angeles' third French mayor, serving two terms. At the same time, his brother Jean-Louis Beaudry was serving as mayor of Montreal.
After finishing his second term, Beaudry bought the local French-language newspaper, L'Union. (I will cover LA-based French newspapers - three or four are known to have existed - at a later date.) Beaudry was already a director of the Los Angeles City and County Printing and Publishing Company.
Nearly all of Los Angeles' Victorian houses have been torn down over the years. However, neighborhoods like Angelino Heights still have Victorian-era homes. Guess who developed Angelino Heights? That's right - Prudent and Victor Beaudry (architect Joseph Newsom designed many of the houses). Carroll Avenue, beloved by preservationists for its high concentration of surviving Victorian homes (kitsch king Charles Phoenix even includes it on his annual Disneyland-themed DTLA tour as "Main Street USA"), is well within the original boundaries of Angelino Heights.
In the 1880s, Angelino Heights was one of LA's earliest suburbs. Cars would not be commonly used for quite some time. To serve the transit needs of potential home buyers, the Beaudry brothers (with several other real estate promoters) built the Temple Street Cable Railroad. This streetcar ran along Temple Street from Edgeware to Spring (it was soon extended to Hoover Street) every ten minutes and ran for 16 hours each day, making transportation fast and simple for residents of Angelino Heights and Bunker Hill. The Pacific Electric Railway eventually purchased the line (switching from cable cars to electric trolleys in 1902), and in time it passed to the Los Angeles Railway. The Temple Street Cable Railroad - far and away the most successful streetcar line in the city's history - ran from 1886 to 1946. SIXTY YEARS. Which is especially impressive considering the Pacific Electric Railway didn't even exist until 1901, and its less-traveled streetcar lines were converted to bus routes in 1925.
Funnily enough, Beaudry had sued the Los Angeles Railway in 1891. He claimed the Railway had excavated First and Figueroa Streets without the proper authority, rendered the streets useless, and blocked access to his property. (He also occasionally sued people who damaged his properties. Can you blame the guy? Building a city is hard work.)
When "Crazy Remi" Nadeau decided to liquidate most of his freighting company's equipment, it was purchased by the Oro Grande Mining Company...which counted Prudent and Victor Beaudry among its shareholders. In the 1880s, the Beaudrys began to take on fewer and fewer projects, but they both remained vocal supporters of developing and improving Los Angeles.
Prudent Beaudry passed away on May 29, 1893, a week after suffering a paralytic stroke (Victor had passed away in 1888, with Prudent acting as executor of his sizable estate). An Illustrated History of Los Angeles County stated:
Prudent Beaudry, in particular, has the record of having made in different lines five large fortunes, four of which, through the act of God, or by the duplicity of man, in whom he had trusted, have been lost; but even then he was not discouraged, but faced the world, even at an advanced age, like a lion at bay, and his reward he now enjoys in the shape of a large and assured fortune. Of such stuff are the men who fill great places, and who develop and make a country. To such men we of this later day owe much of the beauty and comfort that surround us, and to such we should look with admiration as models upon which to form rules of action in trying times.Beaudry died a wealthy man (despite losing his fortune FOUR times), but ironically, he might have died even wealthier. A 1905 article in the Los Angeles Herald stated that nearly forty years previously (i.e. in the 1860s), he had begun to dig a well on one of his hilltop properties. After several hundred feet, he struck a deposit that "looked and smelled like tar." He promptly abandoned the half-dug well. That's right - Beaudry struck oil. But he wasn't looking for oil and had no use for it. Had he made the same discovery a few decades later, things may have been a little different.
The late Mayor's body was returned to his native Quebec. Like the rest of his family, he is buried at Notre Dame des Neiges (Canada's largest, and arguably most beautiful, cemetery). He never married and had no children, so his estate went to the other Beaudry siblings and their families.
Prudent Beaudry's importance as an urban planner and city developer is almost completely forgotten today. His work lingers in the names of Beaudry Avenue, Bellevue Avenue, and various other French-named streets in tracts he developed long ago. (Hill Street was once called Montreal Street in honor of the brothers' hometown - it isn't clear when it was renamed.)
(And, thankfully, Angelino Heights is still standing. I will lose my last remaining shreds of faith in humanity if something bad happens to those precious few surviving Victorians.)
Monday, June 27, 2016
The Incredible Sainsevain Brothers
There were four Sainsevain brothers in all, but two of them - Pierre and Jean-Louis - had a strong impact upon Los Angeles and other areas of California.
Their mother, Marie Vignes Sainsevain, was the sister of Jean-Louis Vignes. In 1838, thirteen years after her brother was compelled to leave France, she sent twenty-year-old Pierre, a carpenter, to California to see if his uncle was even still alive. Eight months after the ship left France, Pierre landed in Santa Barbara and continued on to Los Angeles.
Jean-Louis Vignes was doing quite well, in fact - so much so that much of the extended Vignes/Sainsevain family relocated to Los Angeles.
Within a year of arriving at the El Aliso vineyard, Pierre was traveling to Santa Barbara, Monterey, and San Francisco by ship, seeking new buyers for Uncle Jean-Louis' popular wine and brandy. He succeeded in making the very first wholesale wine transactions in the history of California. The following year, he was running Uncle Jean-Louis' sawmill near San Bernardino.
Bigger things were in store for Pierre: in 1843, Governor Manuel Micheltorena granted him Rancho Cañada del Rincon en el Rio San Lorenzo - nearly 6,000 acres in what is now Santa Cruz County. California was still part of Mexico, and normally land grants were only given to Mexican citizens. Pierre did become a naturalized Mexican citizen in 1844 (he is sometimes referred to as "Pedro Sainsevain"), and Governor Pio Pico confirmed the grant in 1846.
In 1843, Pierre built a sawmill near the rancho with another French carpenter, Charles Roussillon, as a business partner. In 1844, he opened a flour mill. In 1845, he married Paula Suñol, daughter of Antonio Maria Suñol (owner of Rancho Los Coches in modern-day Santa Clara County). In 1846, Pierre and Roussillon built a schooner, the Antonita, on the beach at Santa Cruz (and sailed her to Hawaii to have a copper bottom installed). Pierre and Paula's son Jose Miguel was also born that year.
Every schoolkid in California knows that gold was discovered near Coloma in 1848. Pierre went to the mines with his father-in-law and Roussillon. Although the mining town of Don Pedro Bar was named for Pierre (he was nicknamed "Don Pedro" as a mark of respect by Spanish-speaking friends), the party soon tired of mining, and moved to Stockton to sell supplies to Gold Rush miners.
The town of Don Pedro Bar no longer exists, but the Don Pedro Dam and Don Pedro Reservoir still bear Pierre's name.
In 1849, Pierre and Roussillon went to San Jose, the original state capital of California, and built a large two-story adobe on Market Square. They intended to run a hotel, but instead, the building became California's first State House. Ever the achiever, Pierre also served as a delegate to the California Constitutional Convention that year.
In 1855, Jean-Louis, an engineer, joined his brother and uncle in Los Angeles, and the family expanded production at El Aliso. The brothers had their own storefront selling Sainsevain Brothers wine in San Francisco by 1857, with a wine cellar producing Champagne (well, California's first sparkling wine, anyway). Pierre even hired Monsieur Debanne, a former Champagne maker for Veuve Clicquot, to make Sainsevain Brothers Champagne. The following year, El Aliso was leading the state in wine production, turning out 125,000 gallons of wine and brandy.
Jean-Louis also had a personal accomplishment in 1855. He went to France to visit his two sons, who he had not seen for nearly seven years (remember, international travel was significantly harder, longer, and more expensive then than it is now). During this trip, he met and married the widow of a sea captain (I can only assume Jean-Louis' first wife had died at some point). Jean-Louis left his younger son, Paul, and his stepson, Charles Lepaon, in France to complete their schooling (many of LA's earlier French families sent their sons to school in France, so this was hardly unusual), but returned to Los Angeles with his older son, Michel, his new wife, and his stepdaughter, Honorine.
Meanwhile, on the business front, Champagne/sparkling wine production is always risky. It's often more cost-intensive than still wine, San Francisco does not get as cold in the winter as the Champagne region does (Champagne's cold winters create a dual fermentation process, which means more bubbles), and in those days it was MUCH more common for Champagne bottles to break or explode.
To make matters worse, the Sainsevains used Mission grapes (which weren't quite acidic enough to get the desired result), the Champagne was only aged for one year (five or six years is customary), and during the first year of production, one out of every five bottles exploded. While it's true that Champagne bottles have always had some risk of exploding, this level of loss is extremely high, and Sainsevain Brothers' employees had to wear protective gear in the wine cellars to avoid being badly injured by flying shards of glass. The Champagne experiment, while seemingly successful at first, ended up costing the brothers $50,000 (about $1.4 million today) and had to be shut down by 1862.
It wasn't all bad news while the experiment lasted - the brothers sold 300 cases a month, shipping some of them to New York and Philadelphia. They sent Champagne to President James Buchanan, who praised its taste and thanked them generously for it in a letter. When the French government opened its Los Angeles consulate in 1860, Sainsevain Brothers Champagne was served.
In 1859, Pierre sold his rancho. Uncle Jean-Louis sold his nephews the El Aliso vineyard for $42,000 - about $1.06 million in 2016 dollars - by far the highest price ever paid for a single property in California at the time. In 1861, with California wines being sold on the East Coast for the first time, another Sainsevain Brothers shop opened - this one on Broadway in New York.
Unfortunately, there were more financial problems: Jean-Louis Vignes' adult children sued their own cousins, accusing Pierre and Jean-Louis of underpaying for their father's vineyard. This may sound hard to believe, considering the brothers paid more for it than anyone else had ever paid for land in California at a time when Los Angeles was still a dusty pueblo, but it did indeed happen, and the brothers lost in court. Pierre and Jean-Louis dissolved their winemaking business and sold El Aliso in 1869. The brothers were so financially devastated by the Champagne failure and the lawsuit that the county sheriff auctioned off their possessions and remaining wine stock to cover their debts. (Trademark documents in the California State Archives suggest that the San Francisco wine store and the rights to the name Sainsevain Brothers were likely sold to another team of vintners, Mercado and Marsh.)
Jean-Louis was a Mason, and according to one source, was the first Grand Master of the city's first Masonic lodge, located in the original pueblo. A different source conflicts with this; the facts may well be lost to history. We do know, however, that he was a major player in Los Angeles' eternal struggle: water.
In 1863, Jean-Louis was awarded a contract to improve the city's primitive water system (and I do mean primitive; zanjas, or open ditches, were still in use). However, it proved so difficult and costly that he quit. Two years later, when another contractor gave up after only eight months, Jean-Louis was offered the contract again.
This time, Jean-Louis called for help: Damien Marchessault, former mayor and Water Overseer, partnered with him. In an area called "The Cornfield", now Los Angeles State Historic Park, Jean-Louis built a dam and water wheel to feed one of the city's first backup supplies of water, the Sainsevain Reservoir (long since replaced by Radio Hill Gardens). He and Marchessault also began replacing the city's first pipes - hollowed-out logs - with iron pipes. Unfortunately, in 1868, severe flooding undid all of their hard work. This final failure would be a factor in Marchessault's tragic death. An improved water system would eventually succeed under Prudent Beaudry, Solomon Lazard (both French), and John S. Griffen (more on that later).
It may be difficult for modern-day Californians to imagine a time when the state didn't have one out of every eight U.S. residents crammed into its boundaries, but in the 1860s, California had a seemingly endless supply of wide open spaces presenting new opportunities. One of them was Rancho Cucamonga.
Pierre bought the Rancho Cucamonga vineyard in 1860, and Jean-Louis began managing it in 1867. The brothers introduced "new and better" varieties of grapes, according to Harris Newmark. However, their vines were destroyed by grasshoppers in 1870 and 1871, causing more financial trouble. Despite several ownership changes, Jean-Louis was kept on as the vineyard's manager. A bottle of his own sweet white wine won first place at the 1877 Southern California Horticultural Fair.
The brothers, undaunted, also built houses in San Bernardino (it isn't clear whether any of these houses still exist; they'd be well over a century old by now).
Pierre moved back to Santa Clara County and produced wine (under the Menlo Park label) successfully. His claret won "Best Wine" at the county fair in 1868. By 1870, he was making 20,000 gallons of wine per year, but he closed the operation in 1874. That year, Pierre and Jean-Louis bought land in Hawker Canyon, building a large stone house and reservoir.
Jean-Louis owned a lumberyard at the corner of Alameda and Jackson Streets, although the dates are unclear (much of Jackson Street is now gone, meaning the corner itself no longer exists). The brothers shipped lumber up and down the California coast via schooner. In 1869, Jean-Louis sold a different property to Eugene Meyer (despite the German-sounding name, Meyer was also French), who built the Aliso Tract on it.
The ever-restless Pierre went to Central America (some sources say Peru) in 1874 or 1875, returning to San Jose in 1880. He began producing wine again, and invented a steam-powered stemmer crusher (a device that de-stems and crushes grapes) in 1882. When Paula died in 1883, Pierre returned to France.
Although I can find no record of Jean-Louis marrying for a third time (hell, I can't even find a record of his first marriage), a court record from 1882 suggests he was married to a Florence Matilda Sainsevain (another source suggests she was Charles Roussillon's sister). The Los Angeles Herald described him as an "old pioneer" in his death notice (2/17/1889).
Jean-Louis died in Pasadena in 1889. Pierre died in France in 1904.
The 1883 Los Angeles City Directory lists an "M. Sainsevain" operating a feed store at the corner of Turner and Alameda Streets. However, there were already so many Sainsevains in Los Angeles by 1883 that it isn't clear who exactly this was. Pierre's son Jose Miguel was sometimes called Michael, and Jean-Louis had a son named Michel (to complicate things further, in French, "M." is an abbreviation of "Monsieur"). I had considerable difficulty fact-checking this entry because there were multiple Jean-Louis Sainsevains in the Sainsevain family, nearly all living in Southern California.
Multiple old maps list Sainsevain family property in Fontana (the city gave it the official address of 14804 E. Summit Ave.). The Sainsevain surname, albeit with a savagely butchered spelling, is sprinkled across the Inland Empire. Etiwanda, Fontana, Jurupa Valley, and Rancho Cucamonga all have places named after the brothers. There was a Sainsevain (spelled correctly) station on the Southern Pacific rail line near Rancho Cucamonga, but I have not yet been able to determine its precise location or its fate.
The Sainsevain brothers led incredible lives - and incredibly, no one remembers them. Case in point: Los Angeles used to have a Sainsevain Street*, but now it's a distant memory just like its namesakes.
*An 1868 map shows Sainsevain Street ran between Aliso and Commercial Streets, with Alameda and Vignes as cross streets. Comparing that map to modern maps, it appears that Sainsevain Street was realigned and incorporated into Commercial Street. As the original location runs very close to what are now freeway ramps, the street was most likely moved/destroyed to make room for the 101.



















